On Wednesday, India prepared for its latest endeavor to land on the Moon, marking a historic moment for the world’s most populous nation as it rapidly approaches milestones established by global space leaders.
Scheduled for a 6:04 pm touchdown near the relatively unexplored lunar south pole, Chandrayaan-3—meaning “Mooncraft” in Sanskrit—seeks to achieve a groundbreaking world first within the realm of space exploration.
The Indian Space Research Organisation yesterday tweeted ISRO tweeted, “The Mission Operations Complex (MOX) is buzzed with energy & excitement!”
If Chandrayaan-3 successfully makes a lunar touchdown and lands its robotic lunar rover in ISRO’s second attempt in four years, India will join the ranks of the United States, China, and the former Soviet Union as the fourth nation to master the technology of soft lunar landings.
Following an unsuccessful Indian lunar mission in 2019, this latest endeavor comes merely days after Russia’s first Moon mission in nearly half a century tragically ended in a crash within the same lunar region.
Back in September 2019, India’s Prime Minister Narendra Modi was seen hugging and patting K Sivan, the former chief of Indian Space Research Organisation as the scientist could not hold back his tears after the space agency lost contact with Chandrayaan 2 lander ‘Vikram’ just when its descent to the Moon was initiated.
The prime minister too was emotional.
However, what was taking birth amid the tears and pin-drop silence in ISRO’s controlling room was perhaps the determination to fight back and rise again.
Former head of the Indian space program, K. Sivan, drew encouragement from the latest photos transmitted by the lander, instilling confidence in the successful culmination of the mission’s final leg.
“It is giving some encouragement that we will be able to achieve the landing mission without any problem,” he told AFP on Monday.
Sivan added that the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) had made corrections after the failure of four years ago, when scientists lost contact with the previous lunar module moments before its slated landing, AFP said.
“Chandrayaan-3 is going to go with more ruggedness,” he said. “We have confidence, and we expect that everything will go smoothly.”
Launched nearly six weeks back amid the cheers of thousands of spectators, the mission’s journey to the Moon substantially contrasts with the swift transits of the Apollo missions in the 1960s and 1970s, which reached their lunar destination within days.
Employing rockets significantly less potent than those utilised by the United States during that era, India’s approach involved multiple orbits around Earth to gather momentum before embarking on its month-long trajectory toward the Moon.
Smooth sailing is continuing
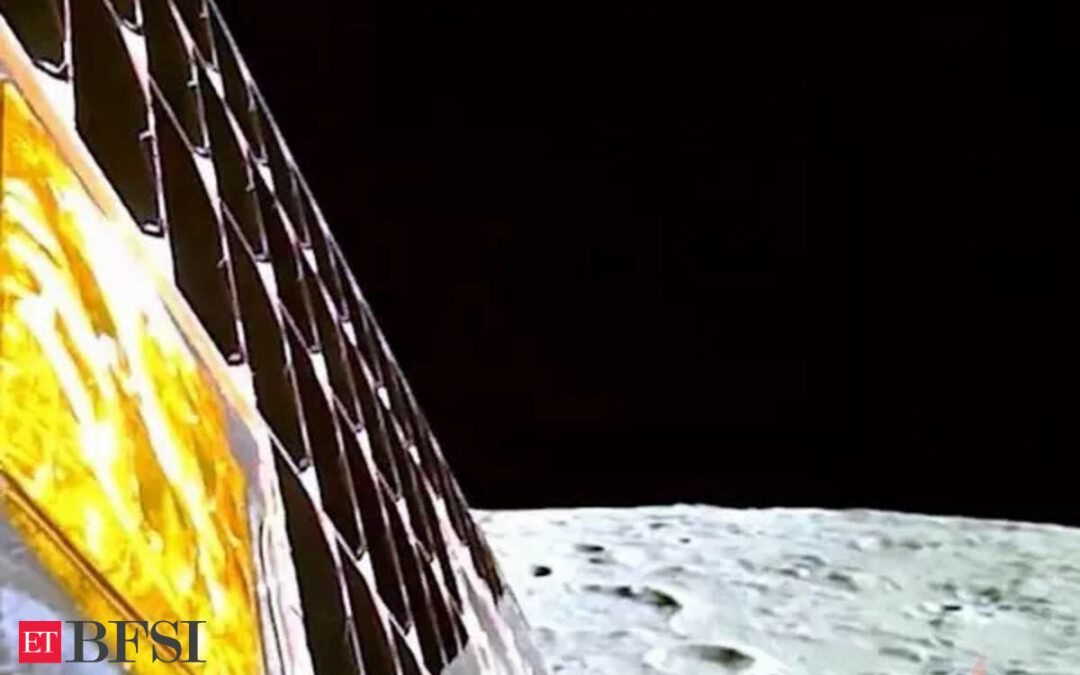
The spacecraft’s lander Vikram, which means “valour” in Sanskrit, detached from its propulsion module last week and has been sending back images of the moon’s surface since entering lunar orbit on August 5.
A day ahead of the landing, the ISRO said on social media the landing was proceeding on schedule and that its mission control complex was “buzzed with energy & excitement”.
“Smooth sailing is continuing,” the agency posted on X, formerly known as Twitter.
India’s space program has comparatively lower budgets than some other countries, but it has been growing a lot since it first sent a spacecraft around the Moon in 2008.
This new mission costs $74.6 million, which is much less than what other countries spend. This shows how India is good at making things work with less money in its space projects.
Experts say India can save money by using ideas and technology that already exist, and by having many skilled engineers who don’t get paid as much as engineers in other countries.
In 2014, India did something impressive by sending a satellite to go around Mars. And they’re planning to launch a mission with people on board that will go around Earth for three days. They want to do this by next year.
‘Very, very important’
Sivan, the former ISRO chief, said India’s efforts to explore the relatively unmapped lunar south pole would make a “very, very important” contribution to scientific knowledge.
Only Russia, the United States and China have previously achieved a controlled landing on the lunar surface.
Russia launched its own lunar probe earlier in August — its first in nearly half a century.
If successful it would have beaten Chandrayaan-3 by a matter of days to become the first mission of any nation to make a controlled landing around the lunar south pole.
But the Luna-25 probe crash-landed on Saturday after an unspecified incident as it was preparing for descent.
Punishing sanctions since the outset of the Ukraine war have affected Russia’s space industry, which has also been beleaguered by corruption and a lack of innovation and partnerships.
(with inputs from AFP)