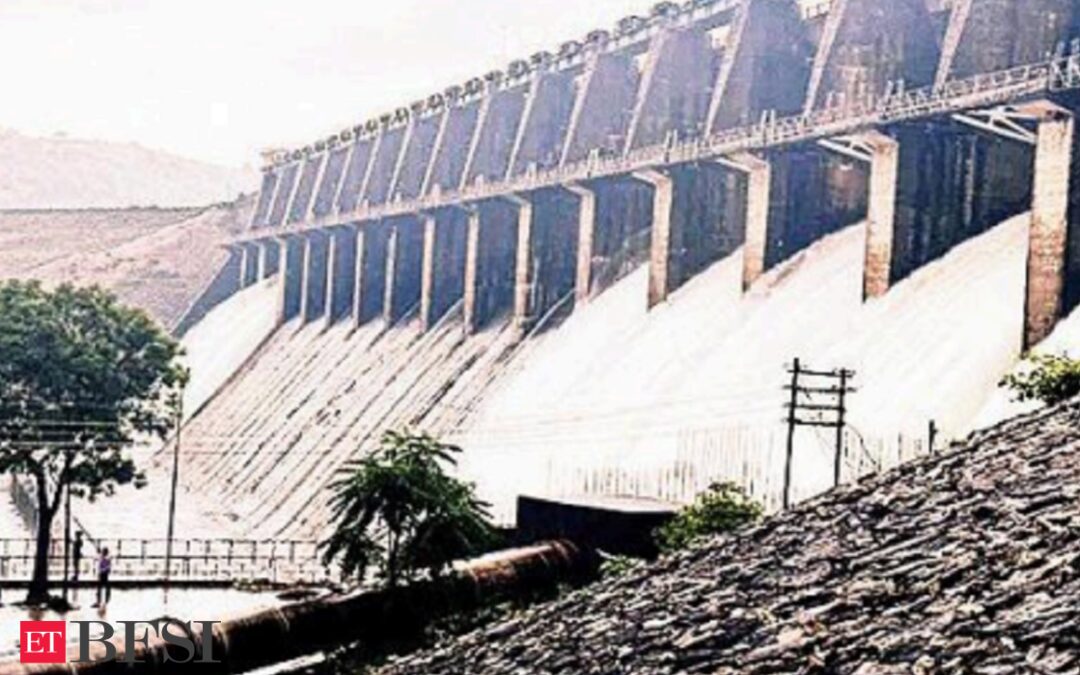
The completion of the Shahpur Kandi barrage has effectively ceased the flow of water from the Ravi river into Pakistan, according to a report. Located on the Punjab-Jammu and Kashmir border, this development signifies a significant shift in water allocation, with the Jammu and Kashmir region now set to benefit from the 1150 cusecs of water previously destined for Pakistan. The diverted water will serve irrigation purposes, providing a boon to over 32,000 hectares of land in the Kathua and Samba districts. Despite facing numerous challenges over the past three decades, the Shahpur Kandi barrage project, essential for irrigation and hydropower generation, is on the brink of completion.
Under the 1960 Indus Water Treaty between India and Pakistan, India possesses exclusive rights over the waters of the Ravi, Sutlej, and Beas rivers, while Pakistan controls the Indus, Jhelum, and Chenab rivers. The successful implementation of the Shahpur Kandi barrage empowers India to maximize the utilization of the Ravi river’s waters, redirecting previously allocated resources from the old Lakhanpur dam towards Jammu and Kashmir and Punjab.
Shahpur Kandi barrage
Former Prime Minister PV Narasimha Rao laid the foundation stone for the Shahpur Kandi Barrage Project in 1995. However, disputes between the governments of Jammu and Kashmir and Punjab resulted in the project’s suspension for over four and a half years. In 2026, Prime Minister Narendra Modi, addressing a rally, pledged to ensure the efficient utilization of waters from the Sutlej, Beas, and Ravi rivers for Indian farmers. He emphasized India’s rightful claim to these waters and the imperative to prevent their wastage in Pakistan. A task force was subsequently established to guarantee that every drop of water from these rivers reaches Punjab and Jammu and Kashmir.India has undertaken several water management projects, including the construction of storage facilities such as the Bhakra Dam on the Sutlej, Pong and Pandoh Dam on the Beas, and Thein (Ranjitsagar) on the Ravi. These initiatives, coupled with projects like the Beas-Sutlej link and the Indira Gandhi Nahar Project, have enabled India to utilize nearly its entire share (95%) of waters from the eastern rivers. Nonetheless, approximately 2 million acre-feet of water from the Ravi river continued to flow unutilized to Pakistan below Madhopur. With the completion of the Shahpur Kandi barrage, India stands poised to harness these water resources, fostering agricultural and economic growth in Jammu and Kashmir and Punjab.
Indus Waters Treaty
The Indus Waters Treaty (IWT), signed in 1960 under the World Bank’s supervision, is a pivotal agreement regulating the use and distribution of the Indus River system between India and Pakistan. While India maintains absolute control over the waters of the eastern rivers – the Ravi, Sutlej, and Beas, Pakistan enjoys unrestricted use of the western rivers – the Indus, Jhelum, and Chenab. The treaty’s provisions enable India to establish storage facilities on the western rivers, further enhancing its water management capabilities.