U.S. President Joe Biden speaks about on the ongoing response to the Key Bridge collapse in Baltimore, Maryland, during brief remarks prior to departing the White House in Washington, U.S., March 26, 2024.
Craig Hudson | Reuters
Maryland Gov. Wes Moore warned Thursday of a “very long road ahead” to recover from the loss of Baltimore’s Francis Scott Key Bridge as the Biden administration approved $60 million in immediate federal aid after the deadly collapse.
Massive barges carrying cranes streamed toward the site to begin the challenging work of removing twisted metal and concrete as a first step toward reopening a key shipping route blocked by the wreckage of the span.
Moore promised that “the best minds in the world” were working on plans to clear the debris, move the cargo ship that rammed into the bridge from the channel, recover the bodies of the four remaining workers presumed dead and investigate what went wrong.
“Government is working hand in hand with industry to investigate the area, including the wreck, and remove the ship,” said Moore, a Democrat, who said quick aid is needed to “lay the foundation for a rapid recovery.” President Joe Biden has pledged the federal government would pay the full cost of rebuilding the bridge.
“This work is not going to take hours. This work is not going to take days. This work is not going to take weeks,” Moore said. “We have a very long road ahead of us.”
U.S. Coast Guard officials said Wednesday night that barges were on their way to the spot where the bridge crossed the Patapsco River, but it was not clear when they would arrive.
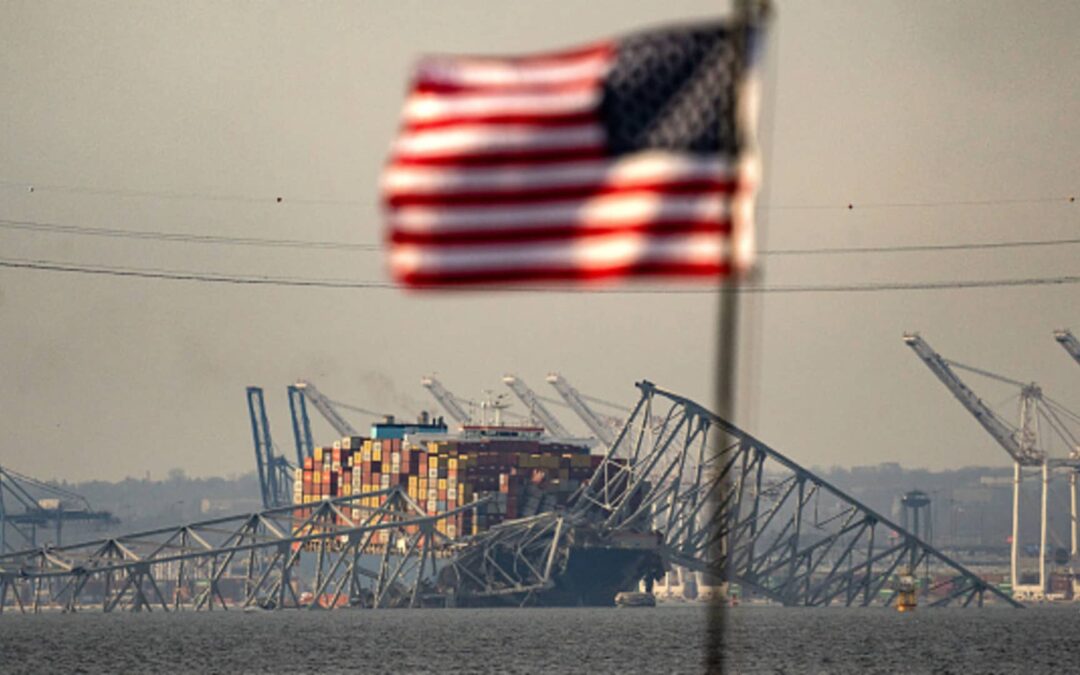
The devastation at the site of the collapse, which happened when the powerless cargo ship struck a pillar supporting the bridge early Tuesday, is extensive. Divers recovered the bodies of two men in a pickup truck near the bridge’s middle span Wednesday, but officials said they have to start clearing the wreckage before anyone could reach the bodies of four other missing workers.
State police said the vehicles appeared to be encased in a “superstructure” of concrete and other debris.
“We have exhausted all search efforts in the areas around this wreckage, and based on sonar scans, we firmly believe that the vehicles are encased in the superstructure and concrete,” Col. Roland L. Butler Jr., superintendent of Maryland State Police, said Wednesday.
National Transportation Safety Board officials boarded the ship, the Dali, to recover information from its electronics and paperwork and to interview the captain and other crew members. Investigators shared a preliminary timeline of events before the crash, which federal and state officials have said appeared to be an accident.
Part of the steel frame of the Francis Scott Key Bridge sits on top of the container ship Dali after the bridge collapsed in Baltimore, Maryland, on March 26, 2024.
Kent Nishimura | Afp | Getty Images
“The best minds in the world are coming together to collect the information that we need to move forward with speed and safety in our response to this collapse,” Moore said Thursday.
Of the 21 crew members on the ship, 20 are from India, Randhir Jaiswal, the nation’s foreign ministry spokesperson, told reporters. One was slightly injured and needed stitches, but “all are in good shape and good health,” Jaiswal said.
The victims, who were part of a construction crew fixing potholes on the bridge, were from Mexico, Guatemala, Honduras and El Salvador, Butler said. At least eight people initially went into the water when the ship struck the bridge column, and two of them were rescued Tuesday, officials said.
The crash caused the bridge to break and fall into the water within seconds. Authorities had just enough time to stop vehicle traffic, but didn’t get a chance to alert the construction crew.
The Dali, which is managed by Synergy Marine Group, was headed from Baltimore to Sri Lanka. It is owned by Grace Ocean Private Ltd., and Danish shipping giant Maersk said it had chartered it.
Synergy extended sympathies to the victims’ families in a statement early Thursday.
“We deeply regret this incident and the problems it has caused for the people of Baltimore and the region’s economy that relies on this vitally important port,” Synergy said, noting that it would continue to cooperate with investigators.
Scott Cowan, president of the International Longshoremen’s Association Local 333, said the union is scrambling to help its roughly 2,400 members whose jobs are at risk of drying up until shipping can resume in the Port of Baltimore.
“If there’s no ships, there’s no work,” he said. “We’re doing everything we can.”
The huge vessel was carrying nearly 4,700 metal shipping containers, 56 of them with hazardous materials inside. Thirteen of those were destroyed, officials said. However, industrial hygienists who evaluated the contents identified them as perfumes and soaps, according to the Key Bridge Joint Information Center.
“There was no immediate threat to the environment,” the center said.
Booms were placed to control the spread of any oil that seeped into the water, and state environmental officials were also sampling the water Thursday.
Commercial divers sent to work beneath the bridge debris and container ship will be met with challenging conditions, including limited visibility and moving currents, one expert said.
“Debris can be dangerous, especially when you can’t see what’s right in front of you,” said Donald Gibbons, an instructor with the Eastern Atlantic States Carpenters Technical Centers.
The sudden loss of a highway that carries 30,000 vehicles a day and the port disruption will affect not only thousands of dockworkers and commuters but also U.S. consumers, who are likely to feel the impact of shipping delays.
The governors of New York and New Jersey offered to take on cargo shipments that have been disrupted, to try to minimize supply chain disruptions.
Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg has said the Biden administration was focused on reopening the port and rebuilding the bridge, but he did not put a timeline on those efforts. Buttigieg planned to meet Thursday with supply chain officials.
From 1960 to 2015, there were 35 major bridge collapses worldwide due to ship or barge collisions, according to the World Association for Waterborne Transport Infrastructure.