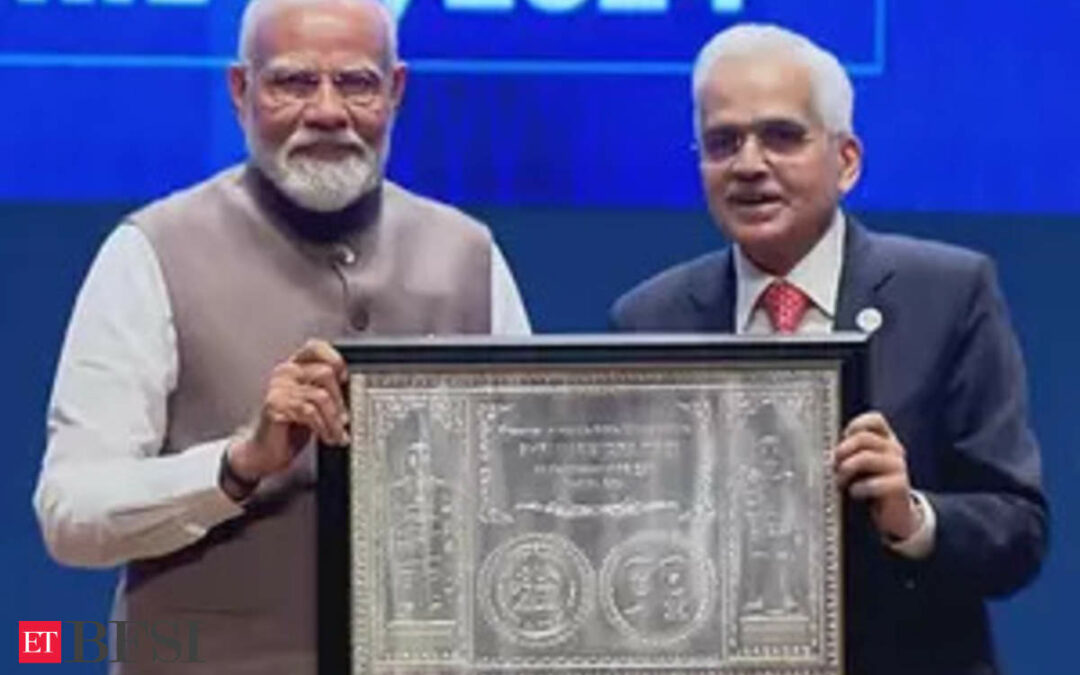
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) celebrated its 90th anniversary with a programme attended by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, who highlighted the institution’s pivotal role in India’s economic growth. As the RBI commemorates this milestone, it is not just reflecting on past achievements but also looking forward to addressing future challenges.
Over the years, the RBI has adapted to changing macroeconomic and regulatory landscapes. Notable among recent developments is the amendment to the RBI Act, which transformed it into an inflation-targeting central bank. Despite initial opposition, this move has enhanced transparency in monetary policy operations, boosting investor confidence.
Room for improvement
While the RBI has demonstrated proficiency in macroeconomic management, there remains room for improvement in banking regulation and supervision. Although non-performing assets (NPAs) have decreased significantly in the banking system, recent episodes such as those involving YES Bank and Infrastructure Leasing & Financial Services Ltd underscore the need for enhanced oversight mechanisms.
Additionally, concerns persist regarding transparency in dealing with regulated entities, as seen in the case of Paytm Payments Bank, experts said. The RBI’s embrace of technology, particularly in payment solutions, has positioned India as a global leader. However, the central bank must navigate the potential pitfalls of technology adoption by fintech firms without stifling innovation.
Looking ahead, maintaining the RBI’s autonomy is crucial for effective functioning. Legal changes empowering the RBI in banking regulation should be considered by the government. Moreover, fiscal discipline is essential to prevent potential fiscal dominance of monetary policy.
Reflecting on its nine-decade journey, the RBI has weathered various economic challenges, from global financial crises to the recent pandemic-induced disruptions. Efforts such as the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) framework have aided in resolving issues like bad loans, paving the way for healthy credit growth.
The formal adoption of inflation targeting and the introduction of Unified Payments Interface (UPI) are among the recent advancements that have bolstered the RBI’s effectiveness. As it sets sights on the next decade, the RBI aims to leverage past learnings, adapt to emerging trends, and continue its crucial role in India’s economic development.