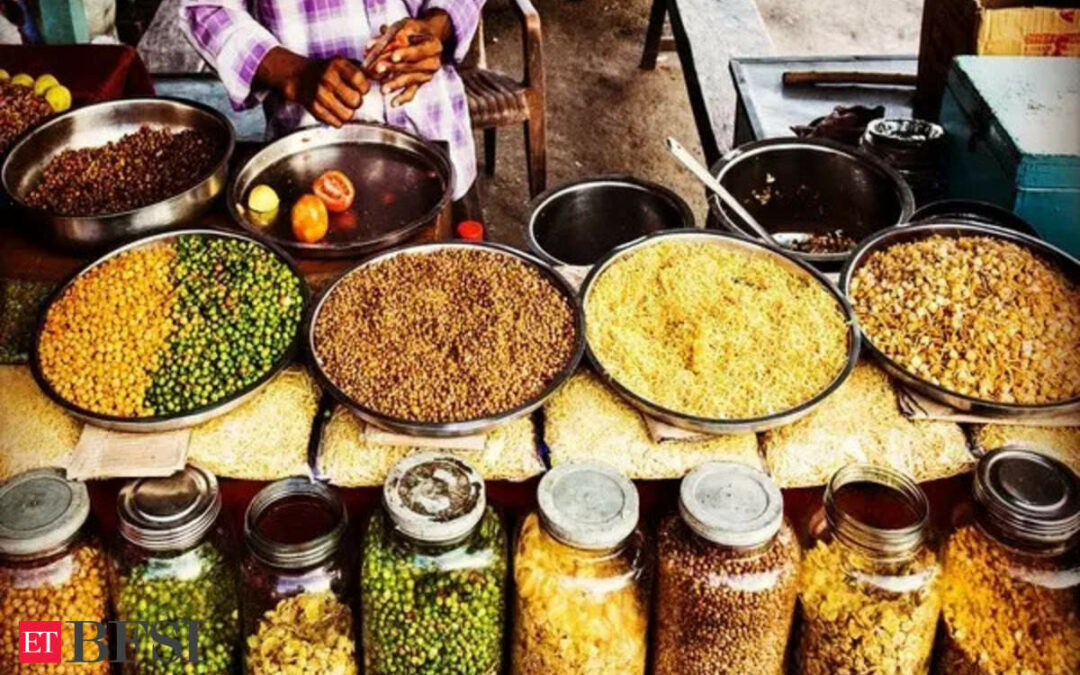
India’s wholesale inflation, measured using the Wholesale Price Index, surged to a 16-month high of 3.36 per cent on an annual basis in June as against a 15-month high of 2.61 per cent last month, government data showed on Monday.
The inflation rate for primary articles stood at 8.80 per cent as against 7.20 per cent in May. The fuel and power inflation witnessed moderated to 1.03 per cent from 1.35 per cent in the previous month.
Manufactured products’ inflation rate rose to 1.43 per cent in June from 0.78 per cent in May. Rate of inflation in the food articles index stood at 8.68 per cent as against 7.40 per cent in May.
“Positive rate of inflation in June, 2024 is primarily due to increase in prices of food articles, manufacture of food products, crude petroleum & natural gas, mineral oils, other manufacturing etc,” said the official press release.
A look at veggies, fruits and pulses
Food inflation remains a sore point for the policymakers as it waits for the “elephant to return to the forest,” as alluded to by the Reserve Bank of India Governor Shaktikanta Das in the latest MPC meeting.
Wholesale vegetable prices increased 38.76 per cent in June 2024, from a contraction of 22 per cent in the same month a year ago. Pulses’ prices increased 21.64 per cent, higher than the 9.21 per cent figure seen a year ago.
The fruit inflation came in at 10.14 per cent against a contraction of 2 per cent in June 2023.
Inflation in wholesale potato prices in June 2024 stood at 66.38 per cent as compared to a contraction of 21.2 per cent last year.
Inflation in wholesale onion prices accelerated to 93.4 per cent in June 2024, up from a contraction of 4.30 per cent in June 2023.
RBI governor Shaktikanta Das on inflation
During the June MPC, RBI Governor Shaktikanta Das said the central bank remains vigilant to any upside risks to inflation, particularly from food inflation which could possibly derail the path of disinlfation.The government also released India’s retail inflation data which showed that it increased to 5.08 per cent from a 12-month low of 4.75 per cent in May.
The Reserve Bank of India increased the repo rate by 250 basis points to 6.5 per cent since May 2022 but has held them at the mark for eight consecutive meetings in a bid to combat inflation. This monetary policy tool typically reduces demand in the economy, helping to lower inflation.
Uncertainties around inflation
The latest RBI monetary policy meeting minutes highlight persistent uncertainties around inflation, particularly from fluctuating food prices, which could impact the inflation outlook. These rising food prices are disrupting India’s current efforts to reduce inflation and pose challenges to achieving the 4 per cent medium-term target.
“Higher food perishables were offset by disinflation in the fuel and broader non-food segments, helping to keep the headline print close to our forecast at 4.8% yoy, the softest print in nearly a year,” said Radhika Rao, Executive Director and Senior Economist, DBS Bank.
This print is likely to be of little consequence for the RBI MPC, which will prefer to take a forward-looking view, opting to see through near-term disinflation in 2QFY and base-effect driven pullback, Rao said.
“The focus will be on the lagged impact of weather-related forces on output, and by extension prices. Core inflation was benign, but is expected to bottom out around mid-year and trend gradually higher thereafter,” she added.