
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) represents a significant shift in the financial ecosystem, aiming to create an open, transparent, and accessible financial system through blockchain technology and smart contracts. This blog explores the core concepts of DeFi, its features, its comparison with traditional finance, the challenges it faces, and its future potential.
What is Decentralized Finance?
DeFi is a financial system that operates without centralized intermediaries such as banks or financial institutions. Instead, it utilizes blockchain technology to facilitate peer-to-peer transactions directly between users. This approach minimizes reliance on traditional financial structures and promotes inclusivity by allowing anyone with internet access to participate in the financial system.
Key principles of DeFi include:
Decentralization: Financial services are distributed across a network rather than being controlled by a single entity.
Transparency: All transactions are recorded on a public ledger, making them visible and verifiable by anyone.
Inclusivity: DeFi aims to provide financial services to individuals who may be excluded from traditional banking systems due to various barriers.
By leveraging these principles, DeFi has the potential to disrupt traditional finance significantly.
Key Features of DeFi
Several features distinguish DeFi from conventional financial systems:
Smart Contracts: These are self-executing contracts with the terms written directly into code. They automate transactions and enforce agreements without intermediaries, enhancing efficiency.
Cost-effectiveness: By eliminating middlemen, DeFi can reduce transaction fees and costs associated with traditional finance.
Accessibility: Anyone with an internet connection can access DeFi services, making it easier for individuals in underserved regions to engage in financial activities.
Programmability: DeFi applications can be built on existing protocols, allowing for innovative financial products that can interact seamlessly with one another.
These features make DeFi an attractive alternative for businesses and individuals alike.
Comparison with Traditional Finance
When comparing DeFi to traditional finance, several key differences emerge:
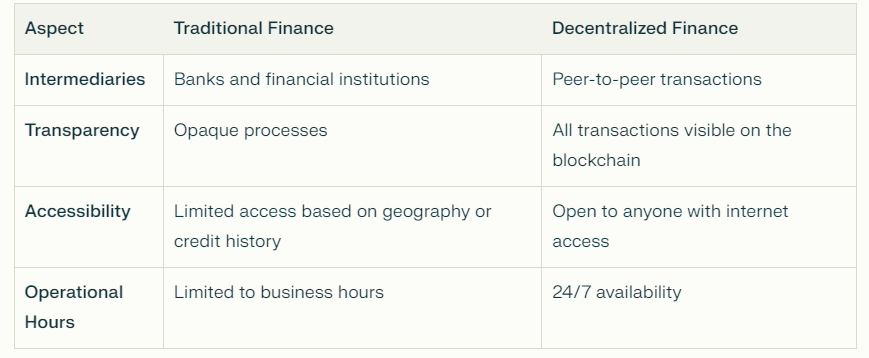
DeFi addresses many limitations of traditional finance by providing more inclusive and efficient alternatives. However, it also faces challenges such as regulatory scrutiny and security vulnerabilities.
Challenges and Risks
Despite its advantages, DeFi is not without challenges:
Regulatory Uncertainty: The evolving regulatory landscape poses risks for DeFi projects. Governments worldwide are still determining how to regulate this new sector effectively.
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Bugs or vulnerabilities in smart contracts can lead to significant financial losses. The immutability of smart contracts means that once deployed, errors cannot be easily rectified.
Security Concerns: The decentralized nature of DeFi makes it a target for hackers. Numerous exploits have occurred due to vulnerabilities in protocols or user error.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for the continued growth and acceptance of DeFi solutions.
How DeFi Promotes Financial Inclusivity and Accessibility
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is fundamentally reshaping the financial landscape by providing unprecedented access to financial services for individuals who have been historically underserved or excluded. This transformation is driven by several key attributes of DeFi that enhance inclusivity and accessibility.
Open and Permissionless Access
One of the most significant advantages of DeFi is its open and permissionless nature. Unlike traditional financial systems that often require extensive documentation, credit checks, and approvals, DeFi platforms allow anyone with an internet connection to participate. This means that individuals from any geographical location can access financial services without needing to go through intermediaries like banks or brokers.
Financial Inclusion for Underserved Populations
DeFi has the potential to bridge the gap for the 1.5 billion adults worldwide who remain unbanked. Many individuals in developing countries lack access to basic banking services due to various barriers, including stringent regulations and high costs associated with traditional banking. DeFi enables these individuals to engage in financial activities such as lending, borrowing, and saving without needing a bank account. This empowerment helps foster economic independence and growth within these communities.
Peer-to-Peer Transactions
DeFi operates on blockchain technology, which facilitates direct peer-to-peer transactions. This eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and allowing users to transact directly with one another. For instance, individuals can lend or borrow funds without relying on a centralized authority, making financial interactions more straightforward and less costly.
Global Accessibility
With its foundation on the internet and blockchain technology, DeFi offers global access to financial markets and assets. There are no geographical limitations; users can engage with DeFi platforms from anywhere in the world. This capability opens up opportunities for cross-border transactions and investments, allowing individuals to participate in global financial markets that were previously inaccessible.
Lower Costs and Fees
DeFi protocols typically operate with lower costs compared to traditional financial institutions. By utilizing blockchain technology and smart contracts, DeFi eliminates many unnecessary intermediaries and associated fees. This reduction in costs makes financial services more affordable for individuals with limited resources, contributing to greater accessibility.
Fractional Ownership
Through tokenization, DeFi enables fractional ownership of assets, allowing individuals to invest in high-value assets that may have been out of reach due to high entry barriers. For example, real estate or art can be divided into smaller units, making it possible for more people to invest in these markets without needing substantial capital upfront.
Programmable Money
DeFi introduces the concept of programmable money through smart contracts. These contracts automate various financial processes, enabling users to set up investment strategies or execute transactions based on predefined conditions. This innovation provides users with greater control over their financial activities and simplifies complex transactions.
Decentralized Identity Solutions
DeFi has the potential to leverage decentralized identity solutions that allow individuals to maintain control over their personal data. This capability enhances privacy and security while facilitating trusted interactions within the DeFi ecosystem. By minimizing reliance on centralized identity verification systems, DeFi promotes inclusivity by allowing users from diverse backgrounds to participate without discrimination.
The Future of DeFi
The future of DeFi holds immense potential for innovation in financial products and services:
Greater Financial Inclusion: As more individuals gain access to the internet, the reach of DeFi will expand, offering financial services to those previously excluded from traditional banking systems.
Innovation in Financial Products: New applications and services will emerge as developers continue to explore the capabilities of blockchain technology. This could lead to novel solutions for lending, insurance, and investment.
While the path forward is promising, it will require collaboration among developers, regulators, and users to navigate the complexities of this evolving landscape.
Conclusion
Decentralized Finance is poised to reshape how we think about financial services. With its emphasis on decentralization, transparency, and inclusivity, it offers a compelling alternative to traditional finance. Businesses seeking innovative solutions should consider exploring the benefits that DeFi can provide.
For businesses looking for reliable DeFi development services, consider partnering with Codezeros for innovative solutions tailored to your needs.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): The Future of Financial Services was originally published in Coinmonks on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.








