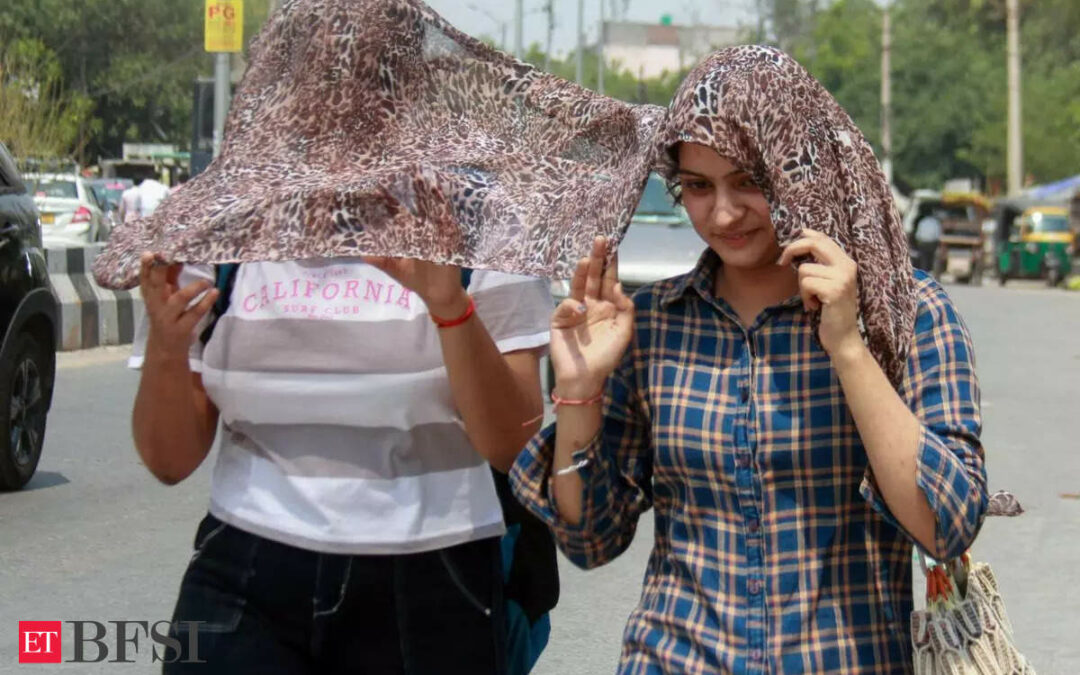
Intense heat waves are not just making daily life inconvenient but also affecting various sectors of the economy. The upcoming monsoon season too will be crucial for the economy. Weather is becoming a permanent factor in the calculations of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) for its power to impact food prices.
The RBI has kept its benchmark interest rate unchanged at 6.5% for more than a year, sticking to a relatively hawkish stance as inflation remains above its 4% target. With uncertainty over prices of vegetables and pulses, the RBI is unlikely to shift its stance anytime soon while expectations of a rate cut have been delayed to the end of the year.
Veggie prices turning hot
The heatwave sweeping some parts of the country is expected to add to the price pressures for vegetables and pulses, which have been on the boil for some time now. Several states in India have witnessed heatwave conditions, with temperatures in some places hovering above 45 degrees centigrade.
Rising demand and tight supplies have seen prices of vegetables soar in recent months, with potato, tomato, onions, ginger and garlic rising sharply and making food costlier for households.
Vegetable inflation has emerged as the most volatile component, thanks to erratic weather conditions such as heatwaves, patchy and uneven rains, and pest attacks which have hurt supplies and pushed up prices.
While overall retail inflation slowed to an 11-month low of 4.8% in April, prices of vegetables and pulses remained stubborn. For example, garlic and ginger prices inflation have ruled in triple digits in March and in April, garlic inflation was at an annual 110.1%, while ginger was at 54.6%. Potato inflation was at 53.6%, onion at 36.6% and tomato at 41.8%.
“The demand for dal and vegetables is continuously rising while supplies are sluggish,” Ashok Gulati, Infosys chair professor at economic think tank Icrier, has told TOI. Prices of veggies are particularly impacted due to adverse weather that shrinks supplies. The heatwave will hit it further,”
High pulse rates
Demand-supply mismatches could keep prices of pulses elevated until the new crop starts arriving in the market in October, putting further pressure on already high food inflation, say experts.
Higher prices of pulses – tur, chana and urad – despite myriad measures to keep them under check have been a cause of concern for the government.
In April, inflation in pulses was 16.8%, with tur at 31.4%, gram at 14.6% and urad at 14.3%. Pulses account for a 6% weight in the food basket and 2.4% in the overall consumer basket for inflation calculation. Food inflation accelerated to 8.7% in April from 8.5% ..
“New crop comes October onwards, and given that tur production was down last year, there would be lower stocks, which will exert pressure on prices,” Madan Sabnavis, chief economist, Bank of Baroda, has told ET. Monsoon’s progress will drive sentiment on inflation in pulses, which will be in double digits till then, Sabnavis said. “Pulses inflation has been in double digits for 11 months and is unlikely to ease until the end of the second quarter of FY24,” Paras Jasrai, senior analyst at India Ratings & Research, has told ET.
This will be one of the push factors for food inflation, Jasrai said, adding: “If monsoon conditions are not conducive, the pulse inflation could stay higher for an even longer period.”
“The next sowing of pulses – mainly tur and urad – will only start in June-July after the onset of monsoon, with harvest for urad happening in October-November while that of tur starting January,” Suresh Agarwal, president of the All India Dal Mill Association, has told ET. The IMD has predicted above-normal monsoon for this year.
The RBI’s food for thought
Pressure in food prices has been interrupting the ongoing disinflation process in India, and posing challenges for the final descent of the inflation trajectory to the 4 per cent target.
Citigroup Inc. economists now see the RBI shifting to a neutral stance only in August rather than its earlier projection of June, Bloomberg reported. “Waiting until August for stance change would help RBI avoid any early market pricing of rates cuts, a better view of monsoon and the global monetary policy dynamics,” Citigroup economists Samiran Chakraborty and Baqar Zaidi wrote in a note. They expect July-August inflation data to be well below 4%, largely due to base effects, providing a more favorable backdrop for the central bank to move.
Upasna Bhardwaj, an economist at Kotak Mahindra Bank Ltd., said erratic weather and heat waves “should keep the overall sentiment cautious” around rate cuts. “We do not expect much change to RBI’s narrative for now as a prolonged pause in policy rates remains the base case,” she said.
A Bank of Baroda report has said that heat-wave conditions have impacted the travel sector with air passenger, diesel consumption and toll collections moderating. However, green shoots are visible in higher auto sales, vehicle registrations and electricity demand.
(WIth inputs from TOI and agencies)