The average salary hike this year will be 9.5%, according to a study of 1,414 companies across 40 sectors by global HR firm, Aon India. However, the averages hide disparities, and increments depend on a range of factors, including the individual’s performance, how relevant his skills are, the company’s financial performance and even the prospects of the sector it operates in. If increments are low, the usual reason assigned by any management is that the company needs to cut costs.
It is a paradox that though companies are forever trying to cut costs, many avoid taking steps that can enhance the income of their employees without adding to the wage bill. If companies restructure their compensation packages by replacing taxable emoluments with some tax-free perks, they can lower the tax liability of their employees. “The salary structure plays a critical role in determining the tax liability of an individual. Many tax deductions and exemptions are not available under the new tax regime, but certain tax-free allowances can be availed of even under the new regime,” says Avinash Godkhindi, Managing Director and CEO of Zaggle Prepaid Ocean Services.
There are several such tax-exempt allowances, including food coupons and reimbursement of expenses on fuel and travel, newspapers and periodicals, phone and Internet. The taxable portions of the salary, such as the special allowance, can be reduced to make place for the tax-exempt allowance. Taxpayers who pay a low rent can consider reducing the house rent allowance (HRA) as well. The HRA exemption is linked to the basic pay and is the least of the following three options: the actual HRA received, 50% of basic pay (40% in non-metros), and actual rent paid minus 10% of basic pay. If you pay a high rent and can claim exemption, keep it high, but if the rent is low, replace it with some other allowance. Taxpayers who live in their own houses and don’t pay rent can also reduce the HRA.
Some of the tax-free emoluments have prescribed amounts, while others have to be within reasonable limits. The reimbursement for conveyance and fuel, for instance, can be very high for employees who need to travel a lot during the course of the day. It is not unusual for a marketing executive to get a conveyance reimbursement of Rs.25,000-30,000 per month, but the employees who are not required to travel can’t expect such a high amount. A growing number of companies have already introduced flexi benefits in their compensation structures. The employee is given the flexibility to design his salary by choosing suitable allowances from a bouquet of benefits.Also Read: Income tax planning for FY 2023-24: Last date is March 31, don’t make these mistakes
Some benefits are taxed differently than others. For instance, an employee can purchase moveable assets (computers, laptops, white and brown goods, even furniture) in the name of the company and get reimbursed for the amount. Under Section 17(2), the employee is taxed for 10% of the value of the asset. So, if you bought a laptop worth Rs.80,000, you will be taxed for only Rs.8,000. In about five years, the book value of the item depreciates to nearly zero and the company sells it to the employee for a nominal sum (usually Rs.1). “IT companies have been offering this to employees for years. Now others have also started offering this benefit,” says Archit Gupta, CEO of tax filing portal, ClearTax.
Companies don’t want to change
Not all companies are willing to take this route. They are reluctant to implement tax-friendly options because they are worried about infringing tax rules and want to stick with what they see as a tried and tested formula. As a result, their employees end up paying a higher tax because of the archaic pay structure. “A company can potentially help its employees save about `1 lakh in tax through these tax-efficient options without incurring any cost or adding to the administrative workload,” says Sudhir Kaushik, CEO of tax filing portal TaxSpanner. “This is equivalent to giving the employee a generous raise without adding a rupee to the wage bill,” he adds.
Companies are also concerned that rolling out these benefits would increase the administrative workload due to the additional paperwork. This is not entirely true. “The flexi benefits in the salary can now be managed digitally, which actually eases the compliance burden for both the employee and the employer,” says Godkhindi. He says the Zaggle card eliminates the need to carry paper-based vouchers or submit them to the employer for claiming reimbursements (see interview, page 5).
Retirement savings as tax-saver
The NPS can be another big tax-saver in the salary package. Under Section 80CCD(2), up to 10% of the basic salary put in the NPS on behalf of the employee is tax-free. It is a voluntary benefit and the employee is free to opt out if he thinks it doesn’t suit him. The NPS benefit can reduce the tax liability of the individual significantly, especially in the higher tax brackets. If your basic salary is Rs.1 lakh, and the company puts Rs.10,000 in the NPS on your behalf, your annual tax will reduce by almost Rs.37,500.
Readers should note that this tax break is over and above the Rs.1.5 lakh deduction under Section 80C and the Rs.50,000 deduction for NPS contributions under Section 80CCD(1b). What’s more, this tax benefit can be availed of even under the new tax regime. “The tax benefits and features of the NPS are unmatchable, but there is very low awareness about the pension scheme among HR professionals,” says Nehal Mota, Co-founder of wealth advisory platform, Finnovate.
This is evident from the lukewarm response to the pension scheme. Though the Section 80CCD(2) option has been there for more than eight years and companies are increasingly opting for this tax-saving opportunity, there are only 19 lakh subscribers under the corporate NPS category. Hyderabad-based financial adviser Nitin Vyakaranam, who provides financial wellness advice to employees of corporates, says barely 5-6% of employees opt for the NPS benefit. This is surprising because tax deductions have traditionally been the biggest driver of investment decisions.
10 perks that can cut tax
If a taxpayer in the 30% bracket gets even 7-8 of these perks, his annual tax outgo can reduce by more than Rs.1 lakh. Some perks have specified limits, but for others the amount should be reasonable. Actual bills are required for tax exemption.
“For some people, saving for a long-term goal that stretches too far into the future is not a priority. They cannot visualise themselves in that situation when they are young,” says Vyakaraman.
Besides the tax breaks it offers, the NPS has everything one may look for in a retirement product. The pension scheme is tightly regulated by the PFRDA, making it very safe and secure. The fund management and other expenses are very low compared to the charges in mutual funds and insurance plans. There is a high degree of flexibility and transparency in the way that the scheme works.
Consultants pay less tax
In recent years, many professionals have opted to leave full-time jobs and become consultants. This gives them some tax advantages, but they also have to forgo the benefits of being a full-time employee. Consultants can claim deduction for workrelated expenses, such as fuel and transportation, telephone, Internet, and even the depreciation of fixed assets. However, they are essentially running a business, so one has to maintain books of accounts and get an audit report in case the gross receipts exceed Rs.25 lakh in a year.
However, the introduction of the presumptive taxation option in 2017 has made things very convenient for those working as consultants. Under Section 44ADA, individual professionals are exempted from maintaining books of accounts. A flat 50% of income is presumed to be expenses and they have to pay tax only on the balance 50%. So, if you are a consultant with an income of Rs.20 lakh, under presumptive taxation, you will be taxed only for Rs.10 lakh.
Consultants are also not eligible for many benefits offered to regular employees, including group health insurance, Provident Fund and all the allowances in a compensation package. All they get is a flat payment after a 10% TDS. This increases the take-home pay for the individual, but financial planners warn against opting for this arrangement. They say regular salaried employment allows one to build longterm savings through the Provident Fund and other terminal benefits.
Consultants also have to spend more time on tax compliance. If gross income exceeds Rs.40 lakh, one has to mandatorily register for GST. This also means filing GST returns every month. At the same time, the GST paid on goods and services purchased for one’s work can be offset against the GST paid by the company.
How much tax can you save?
Restructuring the salary can lead to a significantly lower tax.
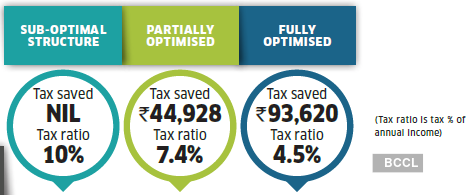
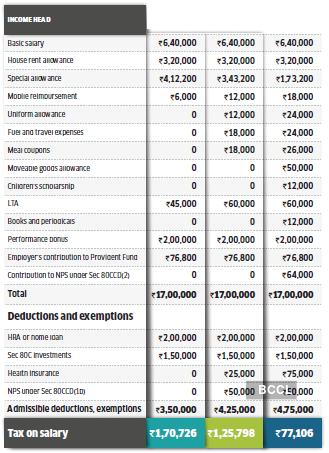
Note1: This is the oldest salary structure with very few allowances and mostly taxable emoluments. The tax outgo is very high for those who work in such companies.
Note2:A higher LTA and some more tax-exempt allowances help bring down the tax to a reasonable level for the employee. But there is scope to save more tax.
Note3: Packing in more tax-free perks lowers the tax outgo. The NPS benefit is the change that makes a big difference. But not many companies offer this benefit.