
Social Media, dominated by Web2 giants, has transformed how we connect and consume information. Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter have amassed unprecedented user bases, their business models revolving around data monetization and targeted advertising. Yet, this centralized architecture has given rise to a host of concerns: from the erosion of privacy to the manipulation of algorithms and the overbearing influence of corporate gatekeepers.
Web3 offers a stark contrast. This decentralized model shifts power from corporations to individuals, placing data ownership firmly in users’ hands. By tapping into blockchain technology, Web3 social media platforms promise a more equitable, transparent, and user-centric digital experience. It is our contention that Web3 social media is not merely a technological upgrade, but a fundamental restructuring of social media, addressing the systemic flaws of its predecessor.
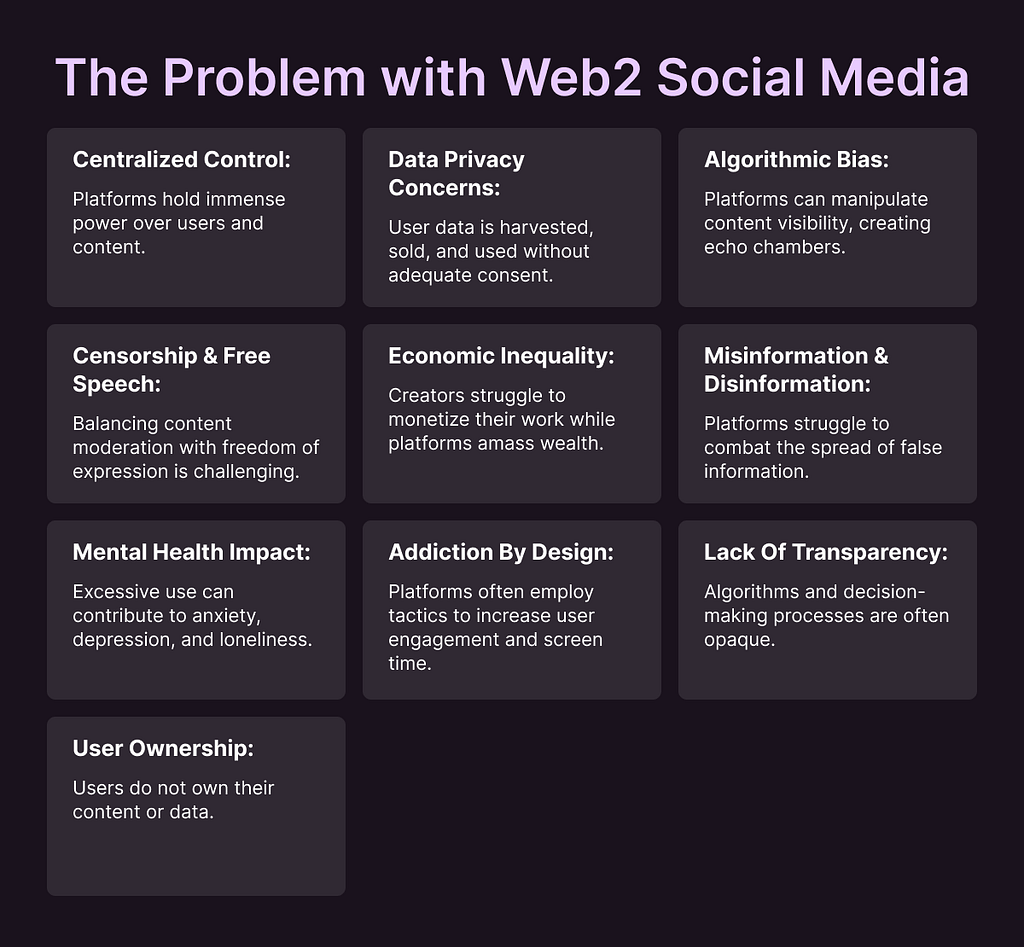
The Web2 Social Media Dilemma
Centralized Control
The centralized architecture of Web2 social media platforms has put unprecedented power on a handful of corporations. These platforms act as digital gatekeepers, dictating the terms of engagement and wielding substantial influence over user experience. From curating the content feed to deciding which accounts to amplify, these platforms maintain unparalleled control. This centralized authority has far-reaching implications, not limited to user experience.
Data Privacy Concerns
A core issue plaguing Web2 is data privacy. User information, from likes and comments to browsing history, is harvested and analyzed to create detailed user profiles. These profiles are then leveraged to target advertising and influence user behavior. While this model has fueled the growth of these platforms, it has also raised serious concerns about privacy. Users often feel like unwitting participants in a surveillance economy, with little transparency or control over how their data is used.
Algorithmic Bias
Moreover, the algorithms that underpin these platforms play a pivotal role in shaping public discourse. Designed to maximize engagement, these algorithms can inadvertently amplify misinformation, promote echo chambers, and limit exposure to diverse viewpoints. The potential for algorithmic bias is a growing concern, as these systems may inadvertently discriminate against certain groups or perspectives.
Censorship and Free Speech
The tension between free speech and content moderation has become a defining challenge for Web2 platforms. While these platforms aspire to be open spaces for expression, they also grapple with the need to protect users from harmful content. Striking the right balance is a complex task, often leading to accusations of censorship or insufficient moderation. The consequences of these decisions can be far-reaching, impacting individuals, communities, and society as a whole.
Economic inequality
The economic dynamics of Web2 social media have created a stark imbalance of power. A small number of platforms generate immense wealth, while the majority of content creators struggle to monetize their work. This disparity has led to calls for fairer compensation models and greater support for independent creators. The platform economy, characterized by its winner-take-all dynamics, has raised questions about economic inequality and the sustainability of the creative ecosystem.
Web3 Social Media Platforms — A Decentralized Alternative

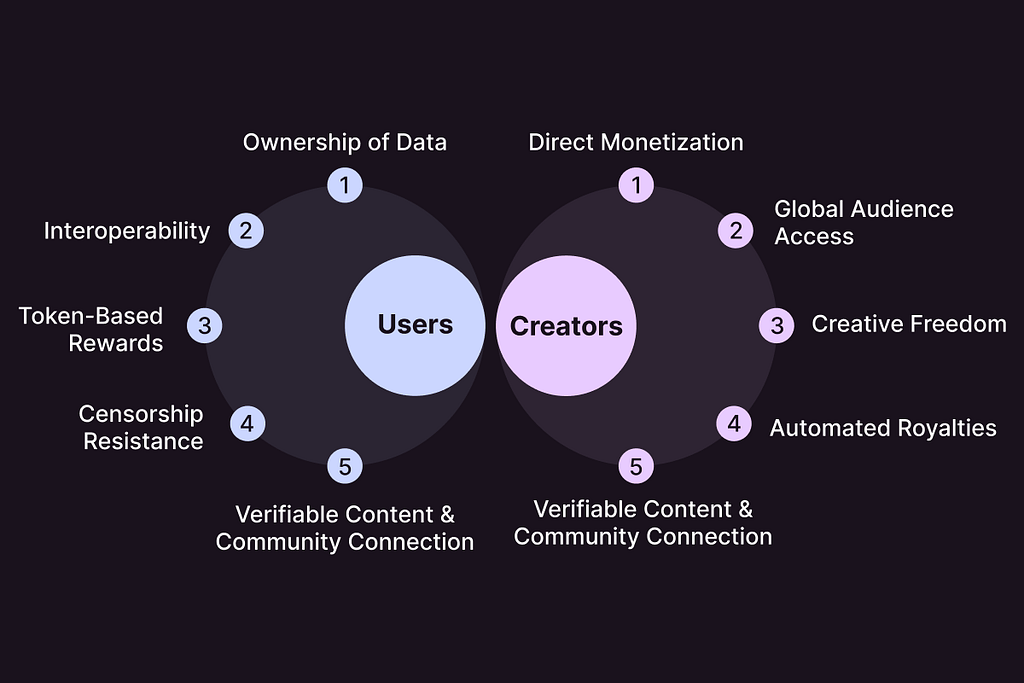
Web3 social media platforms operate on fundamentally different principles compared to their Web2 counterpart. Decentralization is the cornerstone, meaning no single entity controls the platform. Instead, power is distributed among users, creating a more equitable digital space. Ownership of data is another key aspect; in Web3, users retain control over their information, preventing its exploitation by corporations. Transparency is vital, with platform operations visible to all participants, building trust and accountability.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology underpins the infrastructure of decentralized social media platforms. This distributed ledger creates an immutable record of transactions, facilitating data integrity and security. By eliminating intermediaries, blockchain promotes trust and prevents censorship. Smart contracts, self-executing agreements with the terms directly written into code, automate processes and enforce rules, improving efficiency and reliability.
Token Economics
Token economics play a vital role in Web3 social media. Platforms often issue their own cryptocurrency, which can be used for various purposes, such as governance, tipping creators, or accessing premium features. Token holders often have a stake in the platform’s success and can participate in decision-making processes. This approach incentivizes community engagement and promotes a sense of ownership.
Interoperability
Interoperability is a defining characteristic of Web3 social media. Unlike their isolated Web2 counterparts, these platforms aim to effectively connect with other platforms and applications. This allows users to transfer data, content, and even digital assets between different ecosystems. Interoperability promotes innovation, competition, and user choice.
How It Works
To get a deeper understanding of the concept of Web3 social media, understanding the underlying technology is crucial. These platforms are essentially built upon blockchain, which is a distributed ledger (in other words, a shared database), where transactions are recorded and verified across multiple computers. Each block in the chain contains a set of transactions, and once a block is added, it cannot be altered or removed. This immutability ensures data integrity and transparency. Cryptographic techniques secure the network, making it extremely difficult to tamper with or hack.
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. They reside on the blockchain and automatically enforce the terms of the agreement. For instance, a smart contract can automatically transfer funds when specific conditions are met, such as the completion of a task or the verification of a piece of data. This automation eliminates the need for intermediaries, reduces costs, and increases efficiency.
Decentralized storage is another critical component of Web3 social platforms. Instead of relying on centralized servers, user data is distributed across multiple nodes in the network. This approach increases data security, as there is no single point of failure. Additionally, it ensures data availability even if some nodes go offline. While decentralized storage offers advantages, it also presents challenges in terms of data retrieval and management.
Scalability and performance have been significant hurdles for blockchain technology, including its application in social media. Processing a large number of transactions efficiently can be demanding. To address this, various scaling solutions are being explored, such as sharding, which involves dividing the blockchain into smaller segments, and layer-two solutions that handle transactions off-chain. As these technologies mature, Web3 platforms will be better equipped to handle the demands of a growing user base.
Addressing Web2 Issues with Web3 Solutions
Data Ownership & Privacy
Web3 social media is set to rectify many of the shortcomings inherent in Web2 platforms. For instance, fundamentally, Web3 is different from Web2 in terms of data ownership. Unlike Web2, where platforms often claim ownership of user data, Web3 places data control firmly in the hands of individuals. Through cryptographic techniques and decentralized storage, users can securely manage their personal information, deciding who can access it and for what purposes. This approach not only improves privacy but also helps users monetize their data if they choose.
Censorship Resistance
Decentralization is the primary pillar of censorship resistance in Web3. With no single entity controlling the platform, it becomes significantly more difficult to suppress content or silence voices. While content moderation remains essential, it is typically handled through decentralized governance mechanisms, promoting fairness and transparency. This approach protects freedom of expression and leads to a more open and inclusive online environment.
Fairer Creator Economy
Web3 can reinvent the creator economy altogether. Through tokenization, creators can directly monetize their content by offering exclusive digital assets or granting fans access to special perks. Smart contracts automate royalty payments, helping creators receive fair compensation for their work. Moreover, decentralized social media platforms eliminate the need for intermediaries, allowing creators to build direct relationships with their audience. This promotes a more equitable distribution of wealth within the digital ecosystem.
Algorithmic Transparency
Algorithmic transparency is another key advantage of Web3 social media. Decentralized platforms can provide users with greater visibility into the decision-making processes that influence content curation. By understanding how algorithms operate, users can make informed choices about the information they consume. This approach helps to mitigate the spread of misinformation and promotes a more diverse and inclusive online experience.
Community Governance
Community governance is a crucial aspect of Web3 social media. Users have a direct say in platform development and decision-making through decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). By holding tokens, users can participate in voting on platform policies, feature development, and resource allocation. This approach encourages a sense of ownership and empowers users to shape the platform according to their preferences.
Challenges and Opportunities
While Web3 presents a promising vision, it also faces significant challenges.
Scalability & Performance
Scalability and performance remain critical hurdles. Processing a high volume of transactions efficiently is essential for a smooth user experience. Although advancements in blockchain technology are addressing these issues, there’s still room for improvement. Achieving the balance between decentralization and scalability is a complex challenge that requires ongoing innovation.
User Adoption
Gaining widespread user adoption is another obstacle. Web3 concepts can be complex for the average user, creating a steep learning curve. To attract mainstream users, Web3 platforms must prioritize user experience, making platforms intuitive and accessible. Educational initiatives and partnerships with established platforms can also help bridge the gap.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory frameworks surrounding Web3 are developing rapidly and present both opportunities and challenges. Many jurisdictions lack clear regulatory guidelines for cryptocurrencies and blockchain-based platforms. This uncertainty can obstruct innovation and investor confidence. However, a well-defined regulatory environment can also protect consumers and ensure fair competition. Tackling this complex challenge will be crucial for the long-term success of Web3 social media.
Conclusion
Web3 social media represents a significant leap forward, promising a more user-centric, transparent, and equitable digital space. By addressing the shortcomings of Web2 platforms, it offers a promising vision for the future of social interaction. While challenges remain, the potential benefits are substantial.
As a leading Web3 development company, we are at the forefront of this shift. Our expertise can help you build innovative social media platforms based on blockchain technology. Let’s collaborate to shape the future of social media together. Contact us today to discuss your Web3 project.
Source — https://www.codezeros.com/how-web3-social-media-solves-the-issues-of-web2-platforms
How Web3 Social Media Solves the Issues of Web2 Platforms was originally published in Coinmonks on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.








