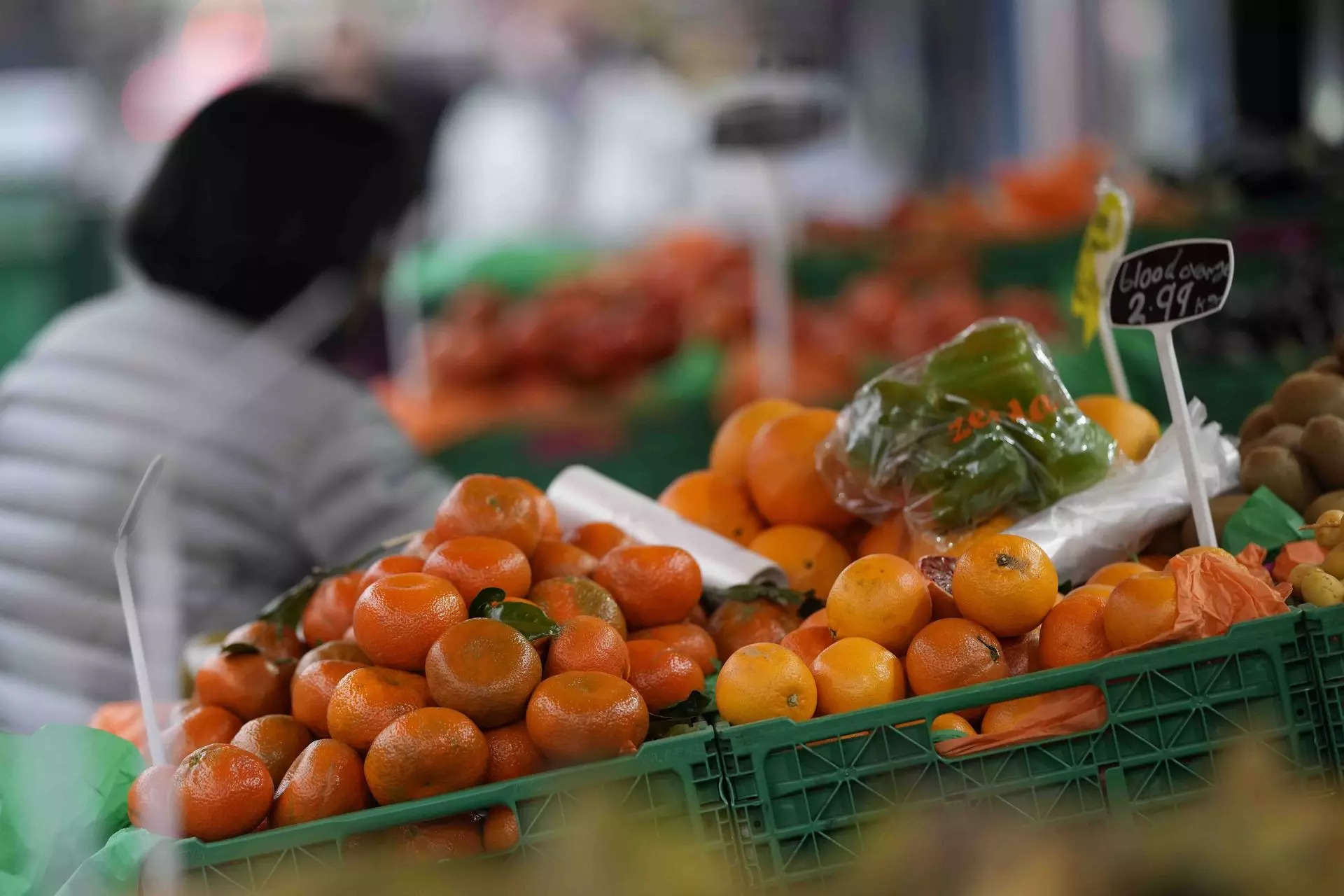
India’s retail inflation eased to 5.02 per cent in September on an annual basis as against 6.83 per cent in August, showed data released by the ministry of statistics on Thursday.
On a monthly basis, the prices deflated (-) 1.13 per cent. The food price inflation for September stood at 6.56 per cent as 9.94 per cent in August. The rural and urban inflation stood at 5.33 per cent and 4.65 per cent, respectively.
Inflation rate for vegetable declined significantly to 3.39 per cent in September from 26.14 per cent in August. Cereal inflation stood at 10.95 per cent in the month of September. The fuel and light segment deflated (-)0.11 per cent in September.
Earlier, Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Governor Shaktikanta Das had expressed the central bank’s anticipation of inflation moderating starting in September. Professional forecasters, comprising economists surveyed by the RBI, projected that the headline CPI inflation will ease from 6.6 per cent in the September quarter to 5.5 per cent in the December quarter. Further projections indicated a decrease to 5.1 per cent in the March 2024 quarter and a range of 5.2-4.0 per cent in the first half of 2024-25.
Regarding core inflation (CPI excluding food and fuel), expectations stood at 4.9 per cent for the September quarter.
Long-term inflation expectations of professional forecasters, gauged by their 5-year ahead projections, have softened to 4.9 per cent, while 10-year ahead expectations remain steady at 4.5 per cent. Based on this, the RBI has set its 2024-25 CPI target at 4.5 per cent, which remains above the mandated target of 4 per cent.
Additionally, the Israel-Hamas conflict adds to the concerns of oil prices exceeding current assumptions, which could subsequently exert pressure on inflation.
In its October meeting, the RBI’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) maintained its inflation forecast for this fiscal year at 5.4 per cent, despite uneven monsoon patterns and a cautious outlook on food prices amidst rising global crude oil costs. The central bank’s projections for Q2, Q3, and Q4 stand at 6.4 per cent, 5.6 per cent, and 5.2 per cent, respectively.
Governor Das pointed out, “The overall inflation outlook, however, is clouded by uncertainties from the fall in kharif sowing for key crops like pulses and oilseeds, low reservoir levels, and volatile global food and energy prices. The MPC observed that the recurring incidence of large and overlapping food price shocks can impart generalization and persistence to headline inflation.”
Furthermore, the MPC unanimously decided to maintain the repo rate, the key lending rate, at 6.5 percent for the fourth consecutive time. The MPC emphasized that the moderation in CPI headline inflation reflects the cumulative impact of monetary policy tightening, supply-enhancing measures, and the full effects of previous rate hikes, which are expected to keep inflationary pressures in check in the coming months.