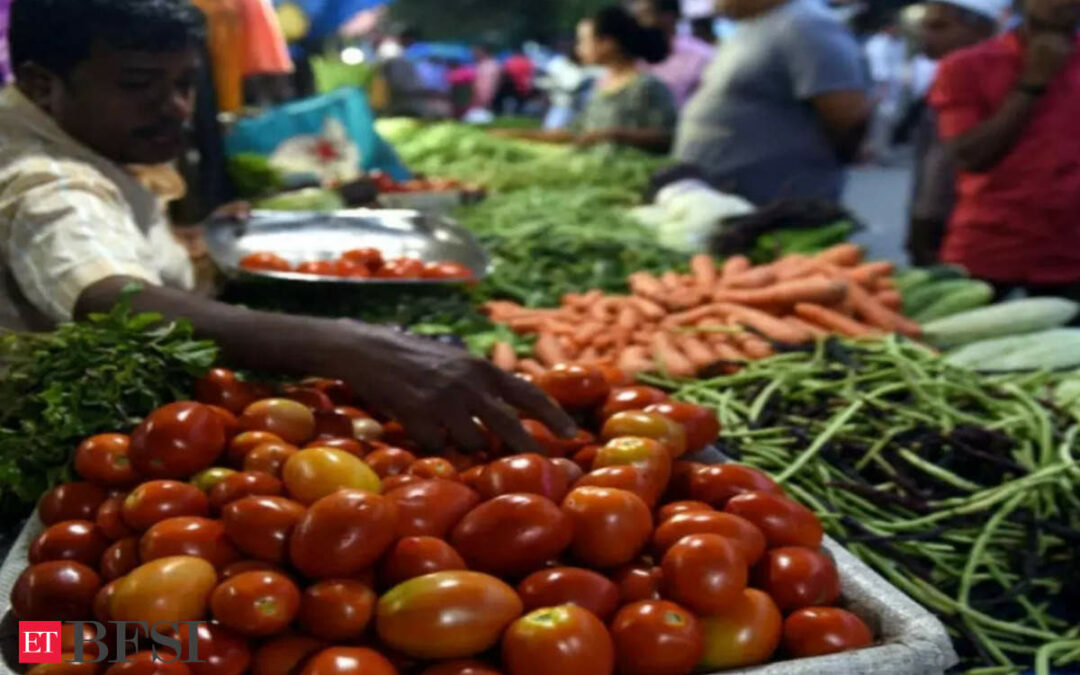
Traditional mathematical models like Phillips Curve, used to predict inflation and forecast its trajectory may not be the best to capture the relation between inflation and its causes, said the economists at The Reserve Bank Of India (RBI). They suggest newer supervised and advanced machine learning (ML) techniques.
In the paper titled ‘Inflation Forecasting in India: Are ML techniques useful’, authors argue that ML techniques outperformed traditional mathematical models for both the pre-pandemic and post-pandemic periods. These advanced machine learning algorithms have performed better at capturing the volatility of inflation during the pandemic. Machine learning is a branch of artificial intelligence (AI) that uses data to imitate a pattern and eventually predict an outcome.
Traditional models can’t capture the non liner and changing relations. And in atypical times like the pandemic, it is not wise to rely on forecasts based only on historical trends.
From the wide array of available ML techniques, the paper suggests only deep learning techniques like artificial neural network and recurrent neural network-long short-term memory. “Deep learning tends to be the most accurate but least interpretable. Linear regression tends to be the most interpretable, and other techniques lie in between these two extremes,” said Nishant Singh and Binod Bhoi, the authors of the paper.
Since the adoption of inflation targeting regime by RBI in 2016, the central bank has been tracking consumer prices in the country. ML techniques can be used to generate consistent and reliable forecasts of inflation which is essential to monetary policy.
“Accurate inflation forecast holds importance for economic agents who form their inflation expectations while negotiating wage-price contracts, and for understanding policy makers’ future reaction in their endeavour to achieve price stability,” said the authors.