
The Blockchain and cryptocurrency industry is seeing a boom like never before, and one of the most noteworthy aspects of this recent rise in popularity is the increase in the number of regular users leveraging on-chain availabilities. The advent of prominent dApps such as Uniswap, OpenSea, etc., has further led to a boost in interaction from users. While this has significantly added to the growth and valuation of the industry, it has also brought some very critical issues to light.
To put things in perspective, though the Ethereum network has vast capabilities and hosts the majority of the dApp activity, there is a lot to be desired in terms of scalability, affordability (in the form of high gas fees), and even accessibility to a certain extent. This is where Optimism, as a Layer-2 scaling solution, is showing great promise, efficiently addressing these issues. As of writing this, by processing a total of over $130 Million transactions as calldata on the mainnet, it has already saved a whopping $4.11 billion in gas fees. Additionally, it holds more than $2.8 billion in on-chain value and counting.
This article aims to thoroughly explore Optimism, how it works, and the key features that play a critical role in enhancing the scalability of the Ethereum network.
What is Optimism
Optimism is a blockchain built as a layer-2 scaling solution for the Ethereum blockchain, functioning on the top of the mainnet or Layer 1. Basically, an optimistic rollup method is utilized to fix Ethereum’s problems, wherein the transactions take place off-chain on Optimism (layer 2). The transaction data, however, is to be posted on the mainnet as calldata (Layer 1) for validation.
To further explicate it, think of Optimism as the assistant chefs in a busy professional kitchen. They gather ingredients (transactions), prepare them, and hand them off to the head chef (main chain) for final gourmet preparation. So evidently, optimism or layer 2 solutions makes it more convenient and affordable to carry out transactions.
If you’re wondering why this scaling method is known as “optimistic”, it is because unless and until conclusive proof of error or manipulation is found, it assumes all transactions processed on layer 2 or off-chain to be valid.
Now that we have got a glimpse of what optimism is, or on a high level, what layer 2 solutions facilitate, let’s explore the mechanics of the optimism chain.
How Does Optimism Blockchain Work?
We have already discussed how the Optimism Blockchain uses the optimistic rollup method, processing transactions in batches instead of one by one. Let’s dive deeper into the working of this layer 2 mini-blockchain.
Block Storage
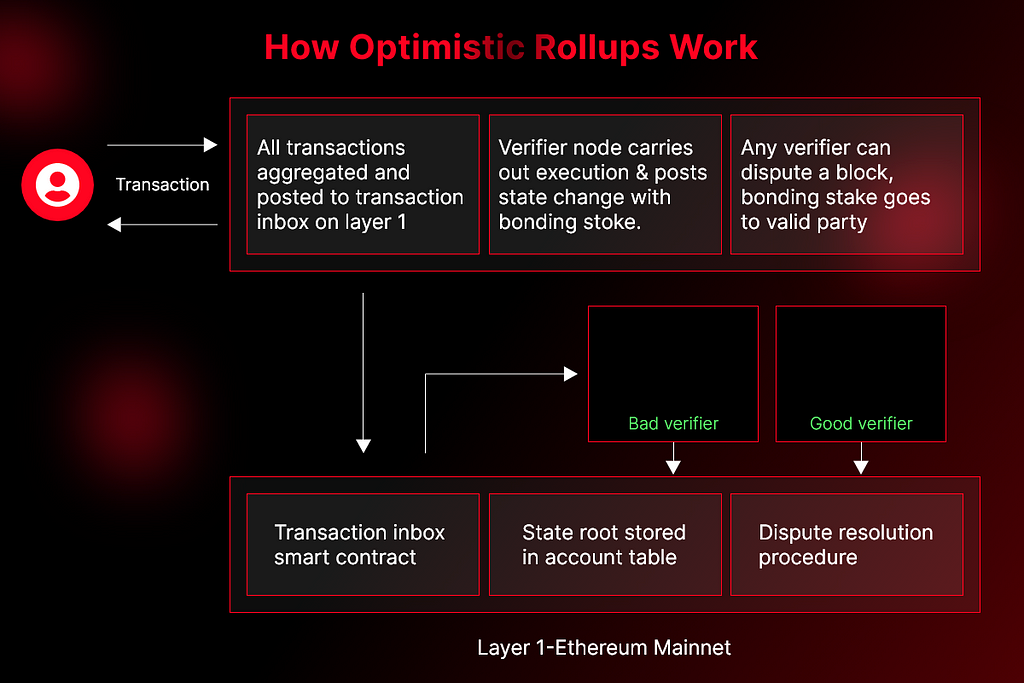
The Optimism Blockchain stores its block on Ethereum using a smart contract called the Canonical Transaction Chain (CTC). The CTC comprises an append-only list of blocks that can only be added to, not changed or removed. Unless the Ethereum network itself goes through a reorganization, the CTC’s code ensures that newer transactions on Ethereum cannot alter the current list of blocks.
Block Production
The Optimism Blockchain produces and processes transactions or ‘deposits’ using a special node called the sequencer. The primary functions of the sequencer include:
- Instantly confirming transactions & updating states
- Producing & executing blocks on layer 2
- Submitting user transactions on the Ethereum mainnet.
After receiving the transactions from the users, the sequencer batches them into blocks. It then utilizes its own virtual machine, equivalent to the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), followed by submitting the blocks to the CTC as calldata — a way of storing data on Ethereum without executing it. The CTC also publishes state roots, which represent the state of the Optimism Blockchain after each block as hashes.
Block Execution
To execute blocks and verify transactions, the Optimism Blockchain utilizes another type of node called the Verifier. It utilizes the state roots or hashes published by the sequencer. It verifies the transactions by comparing them with the state roots it calculates by replaying the transactions on its own virtual machine. If they match, it indicates that the transactions are valid and consistent. In case they don’t, it means the transactions are invalid or there is a discrepancy in the state. In such an event, the verifier can challenge the sequencer by submitting fault proof to the Ethereum chain and claim a reward.
The assumption that the transactions are valid can be challenged within seven days (commonly called the Challenge Window) of the state commitment. A challenger can typically utilize Ethereum’s data availability and the sequencer’s Merkle root to identify errors or manipulations during the challenge window.
Security Mechanism
When it comes to addressing security challenges and risks, Optimism is currently working on two primary issues: Smart contract security risks and protocol upgrades.
Concerning smart contract security issues, while Optimism has undergone several audits, it doesn’t guarantee a bug-free protocol. However, the protocol is offering a $2 million bounty if the whitehats can find bugs in a codebase.
As far as protocol upgrades are concerned, optimism currently uses a centralized mechanism, wherein fast upgrade keys are used to make quick changes to the protocol. While this allows the team to fix any issues or improve protocol faster, it goes against the principle of decentralization, as the team exercises a lot of power and control over the protocol. Having said that, Optimism is working towards adopting a more decentralized and secure upgrade mechanism through multi-client architecture and ZK rollups.
Comparing Optimism and ZK Rollups
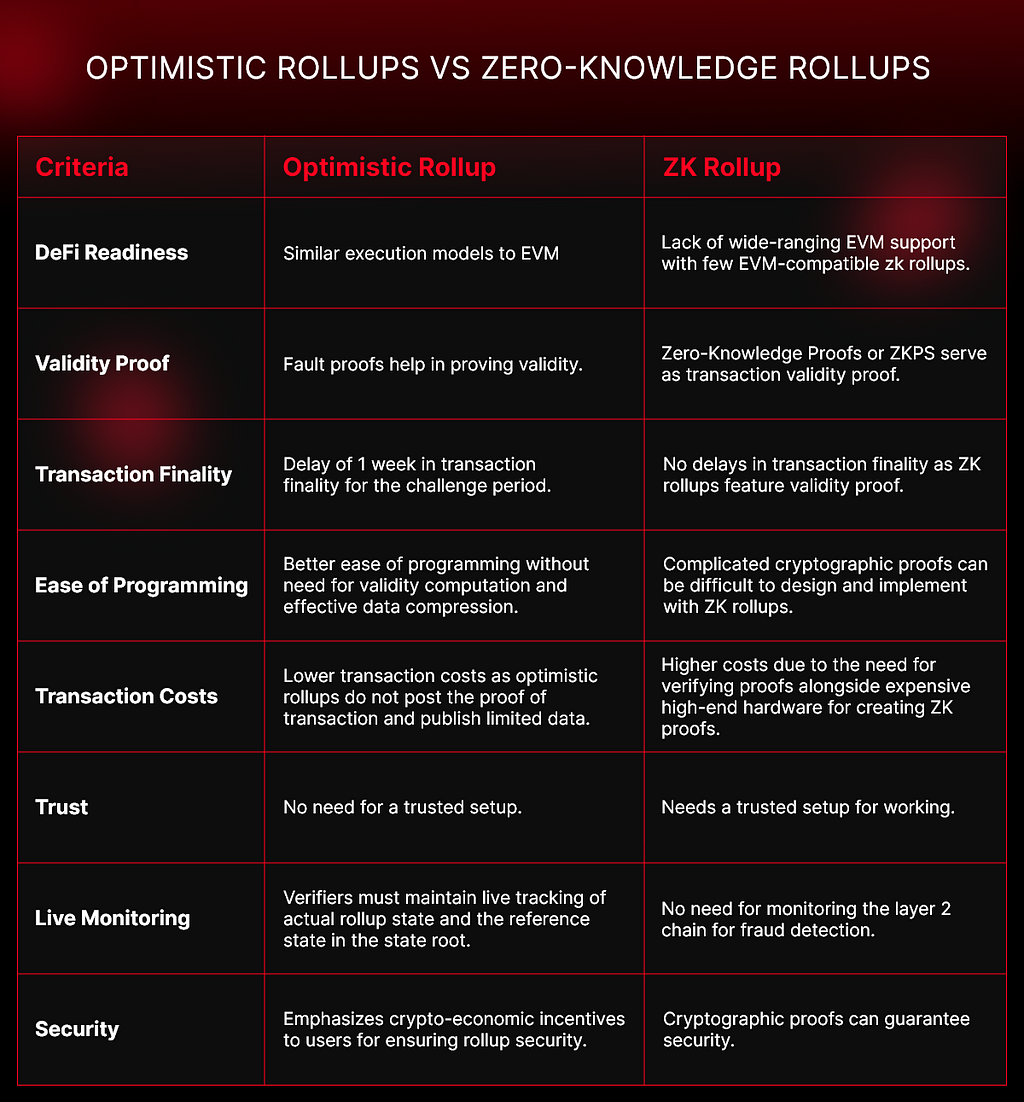
With regard to ZK and optimistic rollup development, the two methods differ in three primary aspects.
This is the most apparent distinction between the two approaches. Optimism rollups assume the transactions to be valid by default unless someone with proof can challenge their validity. ZK rollups, on the other hand, verify the validity of every transaction with a cryptographic zero-knowledge proof before submitting it to the main chain. This indicates that optimism rollups tend to process transactions faster and cheaper but are more vulnerable to attacks and disputes. Essentially, optimism rollups can lead to delayed or reverted transactions while ZK-Rollup scaling solutions are more secure and final.
Optimistic rollups have a longer withdrawal time as compared to ZK rollups. This is because they have to wait for the challenge period to complete before confirming the transactions on the main chain. ZK rollups, on the other hand, can confirm transactions almost instantly, all thanks to zero-knowledge proofs. However, this also signifies that ZK-Rollup scaling solutions have higher computational and storage requirements, affecting their scalability and efficiency.
As opposed to the fault proofs of optimism rollups, zero-knowledge proofs are more self-contained and trustless. However, they also require more advanced cryptography and mathematics, limiting their availability and accessibility.
Understanding the Optimism Token
The Optimism Token, or OP for short, was launched in May 2022 and serves as the native and governance token of the Optimism blockchain. Optimism operates on a democratic, community-driven governance system called the Collective. The community members can utilize the OP token for two main functions, namely governance and public goods funding through the Token House and Common House respectively.
The Token House
It is the Collective’s governance arm, wherein OP holders can use the tokens to vote on how the Optimism network is developed and managed. This includes proposals such as upgrading the protocol, adjusting inflation, managing the treasury, allocating grants, etc.
The Common House or The Citizen’s House
This arm involves OP holders supporting the projects that benefit the Ethereum ecosystem, such as developing tools, researching new solutions, and creating new applications. Essentially, in the Common House, the token holders can come together to propose, discuss, and vote on numerous retrospective public goods that require funding.
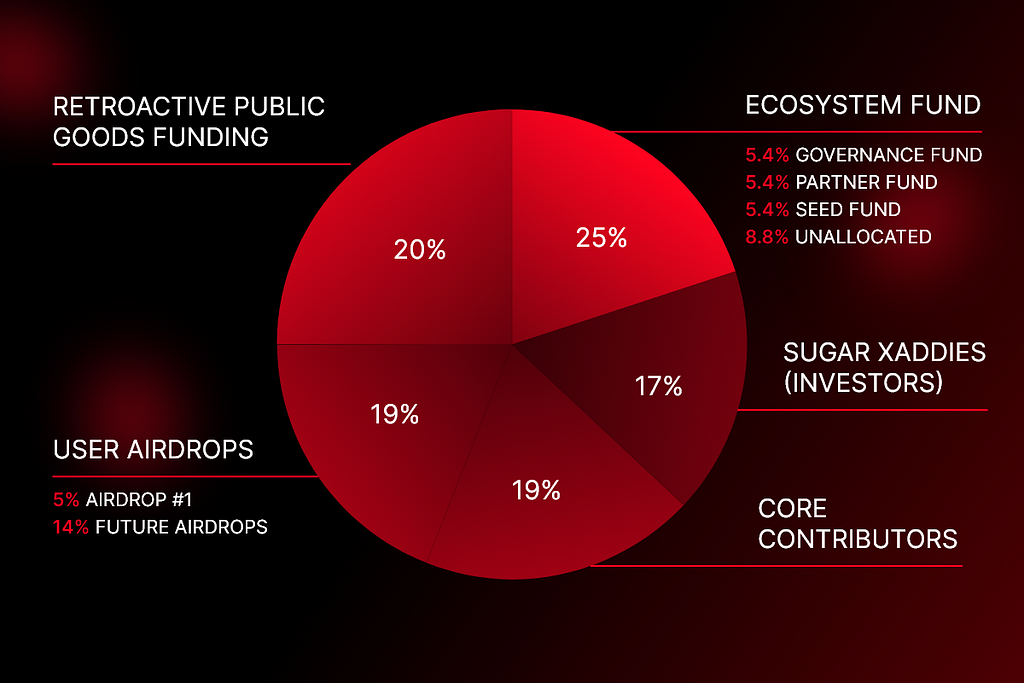
Moreover, talking about Optimism tokenomics, the initial total supply in circulation is about 4.3 billion OP tokens (4,294,967,296 to be precise). This initial supply will inflate at a rate of 2% per year. Also, the initial distribution of OP is shown below:
Noteworthy Features of Optimism Blockchain
Optimistic Rollups
As we have already discussed, the Optimistic blockchain facilitates optimistic rollup development, wherein the transactions can be bundled or “rolled up” into a single transaction that is verified and settled on the Ethereum mainnet. This scaling technique reduces the load on the Ethereum mainnet, effectively lowering the gas fees for users.
Full Compatibility
One of the key benefits of Optimism blockchain is that it supports any smart contract or dApp that runs on Ethereum. Since Optimism utilizes the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) as its execution environment, developers need not make any compromises or code changes and can deploy it using Ethereum languages such as Vyper and Solidity.
Instant Confirmations and Withdrawals
Typically, Optimism does not rely on centralized intermediaries or bridges and provides instant confirmations and withdrawals for users. However, the speed of confirmation varies with different uses. For instance, it takes about 15 minutes for deposits from Ethereum to Optimism to come through, while transferring the assets from Optimism to Ethereum might take the entire Challenge Window period (7 days), owing to the fault-proof verification model.
Decentralized Governance
With the OP token as its native token, Optimism allows community participation and decision-making. The Optimism Collective community aims to create a more sustainable and inclusive future for Ethereum and the crypto space by funding and supporting public goods. It is composed of token holders, builders, and users, making it a diverse and vibrant ecosystem.
By rewarding public goods in retrospect rather than in advance, the Collective ensures that the projects that have proven their value and impact to the community receive more funds. Furthermore, it works on the profitization of public goods and strives to create new business models and incentives that align the interests of the public good providers and the users.
Interoperability with The Superchain
Optimism aims at introducing a superior architecture called the Superchain, representing a more advanced form of interoperability between blockchains. The idea is that the Optimism mainnet can be bound to form a single chain with any other blockchain like Bitcoin, Polkadot, or Cosmos. This leads to a more seamless and secure cross-chain experience for users, developers, and protocols, without comprising scalability, compatibility, and decentralization. However, the Superchain is not yet a reality, but a work in progress, since it faces several social and technical challenges.
The Optimism Blockchain Use Cases
As a layer-2 scaling solution, the Optimism blockchain has quite a few use cases that have attracted the attention of numerous projects.
DeFi: By enabling faster and cheaper transactions, Optimism has proven useful for various DeFi protocols and applications, such as Uniswap, Synthetix, and more. In fact, there are about 140 different DeFi projects currently building on the Optimism blockchain. Moreover, being EVM-compatible, Ethereum-native DeFi protocols such as Curve, Aave, and Perpetual are all deployed on it. At the same time, there are other protocols like Arcadia Finance that are majorly built on Optimism.
Optimism can also support cross-chain interoperability and composability for DeFi users and developers. For instance, prominent bridges like Wormhole, Across, and Stargate are all supported by it.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Optimism can substantially benefit NFT platforms by helping reduce the gas fees and latency for minting, trading, and transferring NFTs on them. This can be reinforced by the fact that more than 40 NFT platforms and projects are deployed on the Optimism mainnet. Additionally, unique NFT protocols like Backed, which supports borrowing and loaning of NFTs, have found their home on the Optimism blockchain.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs): Optimism has facilitated the creation and governance of as many as 12 DAOs so far. Some of the examples that use Optimism are Layer2DAO, MakerDAO, and DAOstar, to name a few. Through DAO, the blockchain also supports the funding and rewarding of public goods in the crypto space.
On-Ramp Solution: By partnering with various FinTechs and crypto exchanges, Optimism has empowered users to buy crypto on the blockchain using fiat currencies like dollars. Through the on-ramp solution, users can utilize credit cards, bank transfers, Apple Pay Transak, Binance, or any of the other 17 onboarded platforms to pay for their purchases.
Tooling dApps: There are several tooling DApps that the Optimism blockchain supports, helping technical as well as non-technical users interact with the Optimism platform and its ecosystem. Some of the prominent examples for technical users or developers include Hop Exchange, Pyth Network, Safe, and Cookbook, while for non-technical users there are no-code protocols such as NiftyKit, which allows creators to launch their NFTs on Optimism.
Deploying A Smart Contract on Optimism
You need to follow these four steps to deploy a smart contract on optimism:
- Use Solidity to write your smart contract code, utilizing any editor or framework you like. You may even use existing templates or libraries if needed.
- Compile your code using the Optimism Compiler, which is a modified version of the Solidity compiler with some added features and checks for compatibility with Optimism.
- Deploy your smart contract on the Optimism network, which only differs from the Ethereum network by the fact that it has its own nodes and tokens. Speaking of tokens, you will need Optimism Eth (OETH) to pay for gas fees. You can get them from faucets or bridges.
- Finally, you can utilize any Web3 library or tool that supports Optimism to interact with your smart contract. Some of the popular examples include Web3.js, Ether.js, or MetaMask.
Wrapping Up
Considering everything, Optimism, as a layer-2 scaling solution, indeed brings in a lot of optimism when it comes to the future of blockchain technology. It addresses the prevalent issues of scalability, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact, thereby enhancing the potential of decentralized applications and solutions. It promises a future where blockchain technology, along with being efficient and scalable, is widely accessible to users around the globe.
There’s no doubt about the fact that with Layer 2 solutions like Optimism being poised to transform the way we interact, transact, and innovate the world of blockchain, it is bringing the dream of a scalable, decentralized future within reach. However, it still requires refinement that the ongoing development is aiming to achieve. So if you’re seeking to leverage the potential Optimism or Layer 2 scaling in general, we, Codezeros, have the right expertise and experience to help you with it. Connect with us today to learn more about our blockchain solutions.
Originally published at https://www.codezeros.com.







