-Riddhima GuptaAs growth drags globally, and the apex bank is making efforts to curb the upsurge in inflation.
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently took a third consecutive pause over the policy rates with retail inflation surged to a 15-month high of 7.44 % in July 2023.
The inflation growth was primarily driven by a rise in prices of vegetables, cereals, pulses, spices and milk and products.
Announcing the policy rates, the governor said our economy has continued to grow at a reasonable pace, becoming the fifth-largest economy in the world and contributing around 15 % to global growth.
Here’s how the Indian economy performed for the month of July on various key parameters:
GST
For the month of July, the GST collection stood at ₹1,65,105 crore. Following the upward trend, records show that it has crossed the ₹1.6 lakh crore mark for the 5th time since inception of GST. It has marked a 11 % y-oy growth this month.
Source : Press Information Bureau
Inflation
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation has witnessed a 2. 57 % upsurge and stands at 7.44 % for July 2023. This is a significant hike from 4.87 % last month, leaving economists surprised, as prices were expected to cool down.
The CPI has gone past the RBI tolerance band of 2- 6 %, and in YoY, has seen a 0.73 % increase. As PM Modi assures the country that efforts to curb inflation will be in motion, the burden of rising prices only increases.
Source : National Statistical Office
FII – DII Data
July once again indicates a fall in Foreign institutional investors (FIIs) and Domestic Institutional Investors (DII) fall as well. FIIs have almost halved in July 2023, compared to last month, currently at ₹ 13,922 crore.
Meanwhile, DIIs went down to ₹ -1,184.33 crore. The blue colour shows FIIs and red colour shows DIIs data.
Source : National Statistical Office
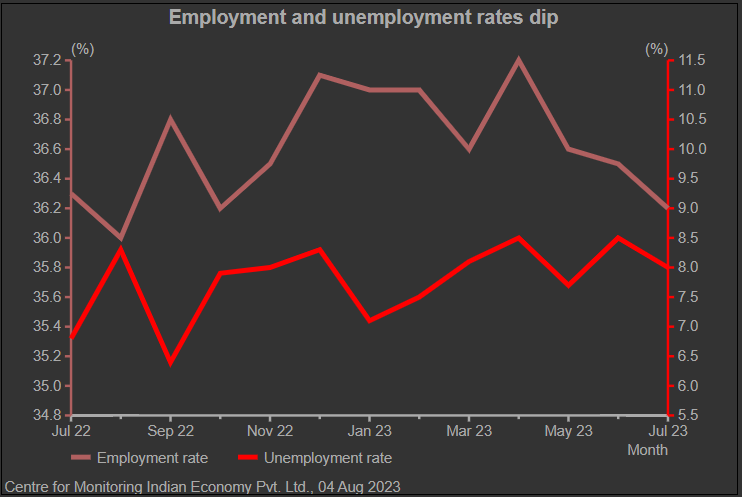
Unemployment
The overall unemployment rate in India is 7.95 % as of July 2023. While the unemployment rate has seen a slight dip from last month, it is still a disappointing number as historically employment rises in July, according to Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE).
Source : Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy
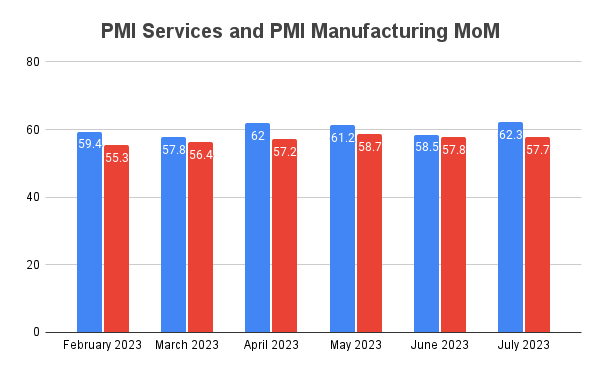
PMI
As has been the case all year, the monthly S&P Global Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) has recorded above the neutral level of 50.0 for both Manufacturing & Services.
PMI Manufacturing posted at 57.7 in July, almost the same as June 2023. Services PMI on the other hand rose to 62.3 in July.
PMI Services is indicated by blue and PMI Manufacturing by red.
Source : S&P Global
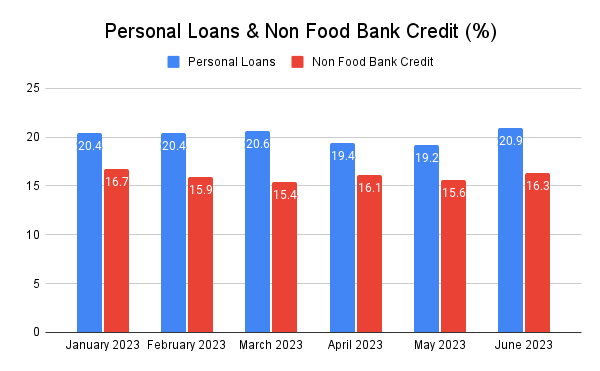
Bank Credit
Non-food bank credit exhibited a growth of 16.3 % in June 2023 as compared with 15 % a year ago.
Services sector accelerated to 26.7 % in May 2023 rising from last month, primarily due to the improved credit offtake to NBFCs and trade.
Personal loans registered a growth of 20.9 % (y-o-y) in June 2023, mainly supported by ‘housing’ and ‘vehicle’ loans.
Credit to industry registered a growth of 8.1 % (y-o-y) in June 2023 as compared with 9.5 % last year. Size-wise, credit to large industry rose by 6.4 % (3.2 % a year ago). Credit to medium industries grew by 13.2 % (47.8 % last year) and micro and small industries by 13.0 % (29.2 % a year ago).
Source : Reserve Bank of India
Trade merchandise
In July of this year, India’s overall (Merchandise and Services combined) exports were USD 32.25 billion, seeing a rise from 38.34 billion in July 2022.
Overall imports in July 2023 were USD 52.92 billion, as compared to USD 63.77 billion in July 2022, exhibiting a negative growth.
Overall trade deficit improves by 45.22 % during July 2023 to USD 8.35 billion from USD 15.24 Billion in July 2022.
Forex & Gold Reserves
Forex reserves for the country are at ₹ 49,82,323 crore as of 4th August, 2023 according to reserve bank. Gold is also a part of the country’s foreign exchange reserves and it stands at ₹ 44,18,603 crore for India.