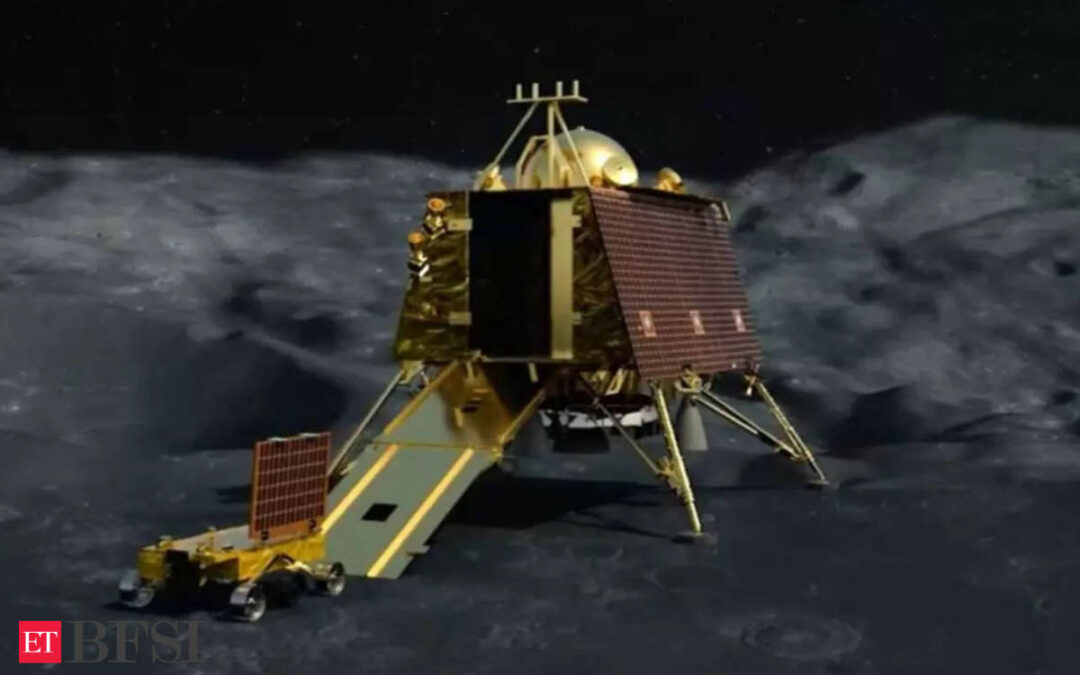
BENGALURU: India is on the Moon! In the next couple of hours, Pragyan the Chandrayaan-3 rover which is sitting in the lander’s (Vikram) belly is expected to emerge and roll out onto the lunar surface. A success at this will make Chandrayaan-3’s more significant.
Earlier in the day, Vikram, the Chandrayaan-3 soft-landed on Moon to propel India into an elite club of nations. It became the first to land a probe in the polar region of the Moon and only the fourth country to land anywhere on the lunar surface.
India has made history four years after success eluded Isro with Vikram in its previous avatar — part of Chandrayaan-2 mission — came crashing down along with a billion hopes.
Vikram performed the powered descent exactly as planned by Isro, going through all the phases — rough braking, altitude holding, fine braking and the terminal descent phase — in a textbook manner to gradually reduce its velocity and orientation to meet the requirements of soft-landing.
And to do this, Vikram was better prepared to overcome challenges of landing this time. So, how different was Vikram from Chandrayaan-2 and what made the difference?
Isro has spent nearly four years — after Chandrayaan-2’s failure to soft-land — anticipating failure scenarios and ensuring they’re addressed.
Learning from this, Isro has implemented several improvements in Chandrayaan-3 to ensure success. And among several changes introduced in Chandrayaan-3, after its predecessor Chandrayaan-2 failed to soft-land on Moon in September 2019, significant are those introduced in Vikram, the lander.
Vikram will have stronger legs than in its previous avatar to enable withstanding landing at greater velocities than earlier.
“There are a lot of improvements on the lander. Basically, what were the deficiencies we were trying to overcome? One is the lander legs, which we expected could have withstood a higher velocity [during Chandrayaan-2]. So how much can we increase the velocity tolerance in the available structure? We have enhanced the landing velocity to 3m/second from 2m/second. That means even at 3m/sec, the lander will not crash or break [its legs],” Isro chairman S Somanath had explained.
Another scientist who was part of Chanrayaan-2 said: “A landing/touchdown velocity of about 2m/second is ideal and safe. And it is good that the tolerance will be for 3m/second, which means in case the best situation is not there, the lander will still do its job.”
The second change is the addition of more fuel to Vikram to handle more disruptions and have the “ability to come back” so there’s more cushion to handle the mission.
“Third, we have added a new sensor called the laser doppler velocity metre, which will look at the lunar terrain. And through laser source sounding, we will be able to get components of three velocity vectors. We will be able to add this to the other instruments available, thereby creating redundancy in measurement,” Somanath had said.
Isro has also improved the software to have more tolerance to failures like engine disruptions, thrust disruptions, sensor failures, etc, while also removing the central or fifth engine, which was added last minute during Chandrayaan-2.
“Five engines were OK with the earlier mass of the lander but now we’ve enhanced the mass by nearly 200kg. Also, given its weight now, we have to necessarily fire a minimum of two engines to do the landing, and cannot land with a single engine. Therefore, the central engine has been removed,” Somanath added.
He added that the space agency has extended solar panels and more panel area to generate power. Vikram will be able to generate power even if it lands in a different orientation and is not facing the Sun. It also has additional TTC (tracking, telemetry and command) antennas for redundancy.
“But the major part of the preparations was dedicated to testing. The whole of the last two years went for testing and not changes. The amount of tests we’ve done is much more than what was done during Chandrayaan-2. This is in terms of autonomous flights, helicopter flights, crane-mode landing simulation tests, drop tests, software simulation testbeds which were newly made to evaluate potential failures and recovery options etc,” Somanath told TOI.