India’s Consumer Price Index recorded a 59 month low at 3.54%, as released by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation on Monday.
Previous month in June, India’s retail inflation stood at 5.08%, alongwith the food inflation at another high at 9.36%.
The CPI numbers for rural and urban came out to be 4.10% and 2.98% respectively.
The retail inflation is well within the Reserve Bank’s range of 2% to 6% for the current fiscal.
“Moderation in CPI was largely on account of a high base from last year (Jul-23: 7.4%). Excluding base effect, headline CPI inflation would have clocked a print of 5.9%, implying that base effect shaved off 240 bps from the headline inflation print in Jul-24,” stated the HDFC Bank Treasury Research report.
The base effect refers to the impact of the previous year’s inflation rate on the current year’s inflation figures. When the base level from the prior year is unusually high or low, it can distort the interpretation of current inflation data.
Movement of Retail Inflation in FY25
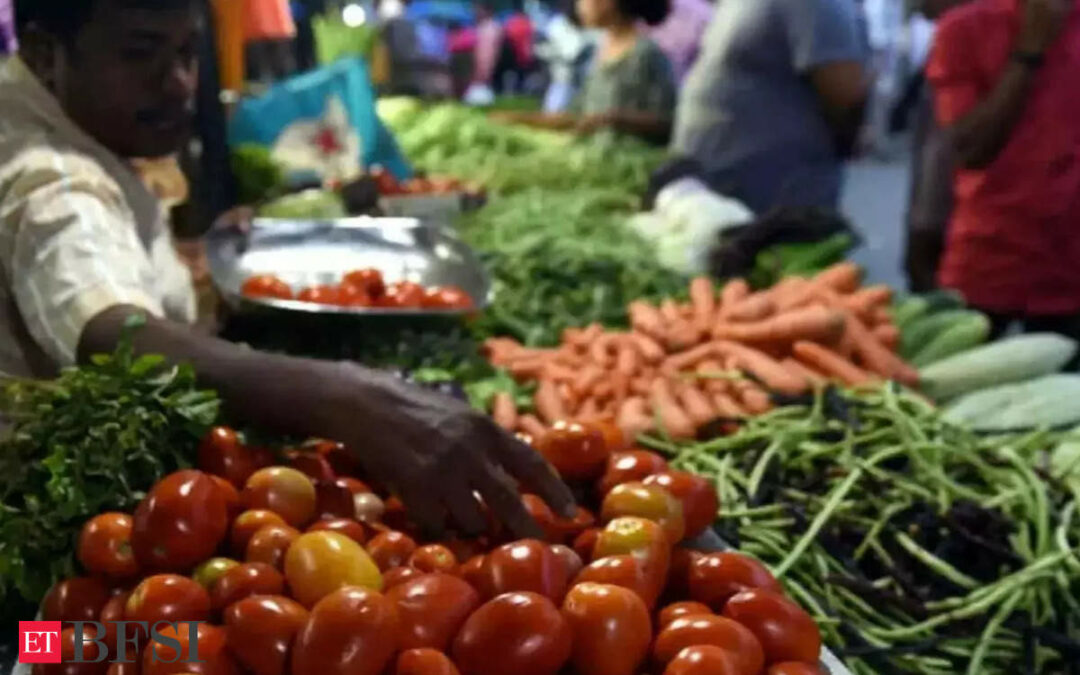
Food Inflation which was a major concern past month has eased to 5.42% in July from 9.36% in June.
Consumer Food Price Index is at 5.89% and 4.63% for rural and urban respectively.
The government release states that there is a decrease in prices of all the groups but the subgroup of vegetables, fruits, and spices recorded a significant decline.
The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation also released the IIP data for the month of June which recorded a growth of 4.2%, which in June 2023 was 4.0%.
“The Indices of Industrial Production for the Mining, Manufacturing and Electricity sectors for the month of June 2024 stand at 134.9, 145.3 and 222.8 respectively,” stated the release on Monday.