Retail inflation, or the Consumer Price Index (CPI) in India, is expected to remain below or close to 5.0 percent in the remaining months of 2024-25, except for September, according to SBI Research.
India’s retail inflation rate increased in June, deviating from the moderation seen in previous months, driven by rising food prices.
The year-on-year inflation rate based on the all-India Consumer Price Index (CPI) was 5.08 percent (provisional) for June 2024. The corresponding inflation rates for rural and urban areas were 5.66 percent and 4.39 percent, respectively.
Twelve states had inflation rates above India’s overall rate of 5.1 percent in June. Odisha recorded the highest inflation rate at 7.22 percent, followed by Bihar at 6.37 percent and Karnataka at 5.98 percent.”With the monsoon progressing satisfactorily and overall seasonal variations balancing out, we do not expect any significant deviation in the inflation outlook,” stated a report from SBI Research authored by Soumya Kanti Ghosh, Group Chief Economic Adviser at the State Bank of India.
Furthermore, with US inflation having declined by 0.1 percent from May, putting the 12-month rate at 3 percent, its lowest level in more than three years, there are grounds for a potential Fed rate cut by September, the report noted.
“We, therefore, feel the RBI will revisit the policy stance around that time in line with our expectations,” the SBI Research report added.
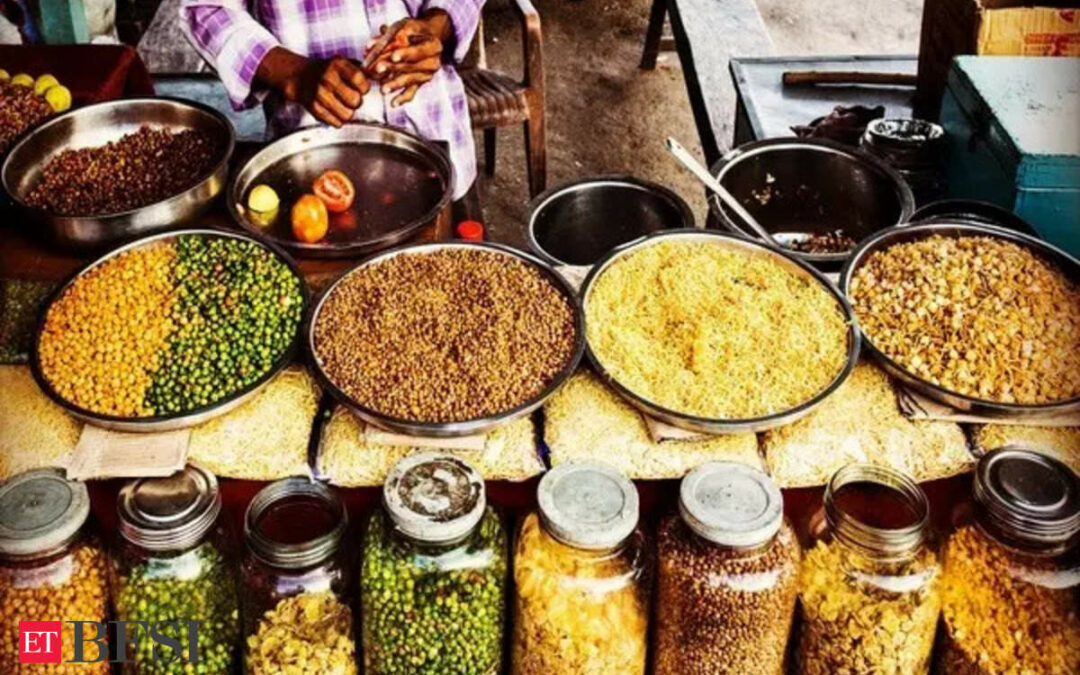
Rising food prices continued to be a concern for Indian consumers, with the inflation rate in the food segment nearly doubling year-on-year in June. Food inflation almost doubled to 8.36 percent last month, compared to 4.63 percent in the same month of 2023, according to data.Government data released on Friday showed that retail inflation for all segments of food–including cereals and products, meat and fish, eggs, milk and products, oils and fats, fruits, vegetables, pulses and products, sugar, spices, prepared snacks, and sweets–rose month-on-month.
Food prices remain a significant challenge for policymakers in India, who aim to bring retail inflation to 4 percent on a sustainable basis.
Annual retail inflation in May was at a 12-month low of 4.75 percent, slightly down from 4.83 percent in April. Retail inflation, or the Consumer Price Index, was 5.7 percent in December last year and had been moderating since.
The retail inflation in India is within the RBI’s 2-6 percent comfort level but is above the ideal 4 percent target.
Inflation has been a concern for many countries, including advanced economies, but India has largely managed to steer its inflation trajectory effectively. The eased month-on-month retail inflation, except for June, followed the RBI’s decision to maintain the status quo on the repo rate for the eighth consecutive time.
Despite the recent pauses, the RBI has raised the repo rate by a cumulative 250 basis points since May 2022 to combat inflation. Raising interest rates is a monetary policy tool that typically helps suppress demand in the economy, thereby helping reduce the inflation rate.
The repo rate is the interest rate at which the RBI lends to other banks. The next monetary policy meeting of the RBI is scheduled for early August.
Pressure from rising food prices has been interrupting the ongoing disinflation process in India, posing challenges for achieving the final descent of the inflation trajectory to the 4 percent target.