
Decentralized exchanges (DEX) have come up as a groundbreaking advancement in the crypto world, and when discussing this transformative technology, one name inevitably rises to the forefront — Uniswap. The platform is the largest DEX protocol and has proven to be a trailblazer in the DeFi ecosystem, introducing innovative concepts like automated market makers (AMMs) and processing more than $1.5 trillion in trading volume.
Since its inception in 2018, it has gone through several iterations or upgrades, with the latest being Uniswap V4. The fourth version of this prominent platform promises a more flexible and customizable experience for liquidity providers (LPs) and traders alike while enhancing cost efficiency. In this article, we will deep dive into the exciting developments in Uniswap V4 and how they impact DeFi users.
Uniswap — A Glimpse into the History
Uniswap was launched in 2018 by Hayden Adams (CEO of Uniswap Labs) as a decentralized exchange protocol that would act as public infrastructure within the crypto ecosystem. It is an Ethereum-based protocol that enables users to swap ERC-20 tokens. Being a DEX, there was no order book or intermediary involved, rather it depended on an automated market maker (AMM) mechanism that utilized smart contracts to ensure liquidity and trading. The fact that it incentivized liquidity providers with trading fees became one of the primary reasons for its exponential growth over the years.
Evolution of Uniswap: from V1 to V3
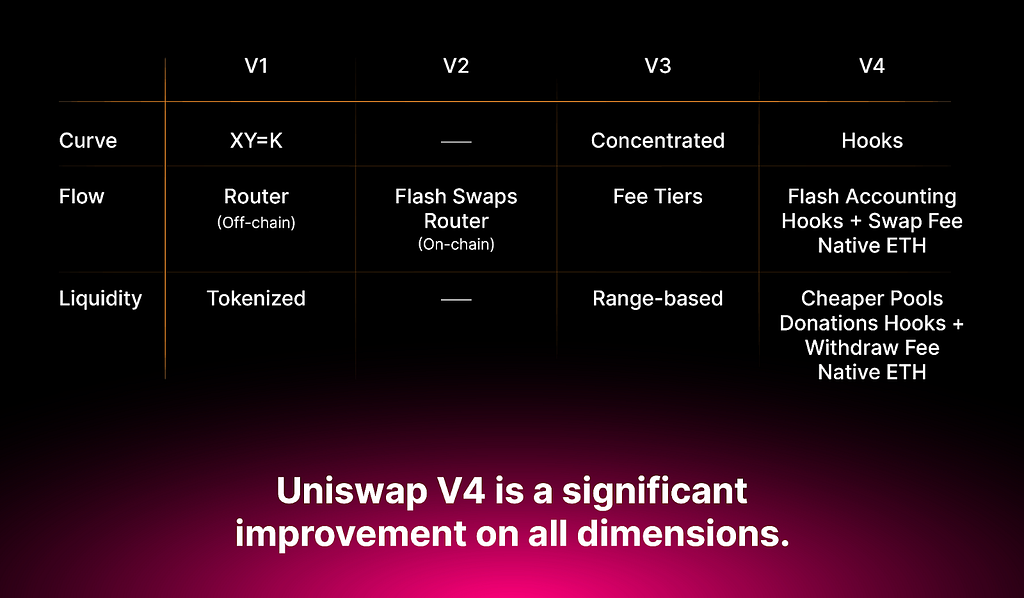
As mentioned earlier, there have been multiple iterations of Uniswap available to users since its launch. The version 1 of the protocol allowed users to swap between ETH and ERC-20 tokens. An upgrade on V1, Uniswap V2 proved to be a massive improvement as it enabled ERC-20/ERC-20 swaps, lifting the restriction present in the previous iteration of the crypto exchange solution. Other notable upgrades of V2 included price oracles and flash swaps.
Now if V2 was impressive, Uniswap V3 took it up a notch. The upgrade’s most stand-out feature was concentrated liquidity. It lets LPs concentrate their liquidity within a price range, allowing them to gain potentially higher returns while requiring lower capital. Other prominent features of V3 include multiple fee tiers (005% — 1%), range orders, non-fungible liquidity, advanced oracles, and dynamic fee switching.
Unraveling Uniswap V4 — the Latest Iteration
While Uniswap V3 provides the LPs with more control over how much risk and reward they want to take when they pool their money and make the system more efficient, the new features invariably lead to higher fees and code complexity. For instance, the use of advanced oracles allowed the system to retrieve real-world and up-to-date information from the real world, such as the prices of different cryptocurrencies. However, the feature made the system more expensive for swappers. Furthermore, as per the on-chain data, actively managing and changing positions didn’t always lead to better performance compared to regular setups. This highlighted the need for improvement.
The Standout Features of Uniswap V4
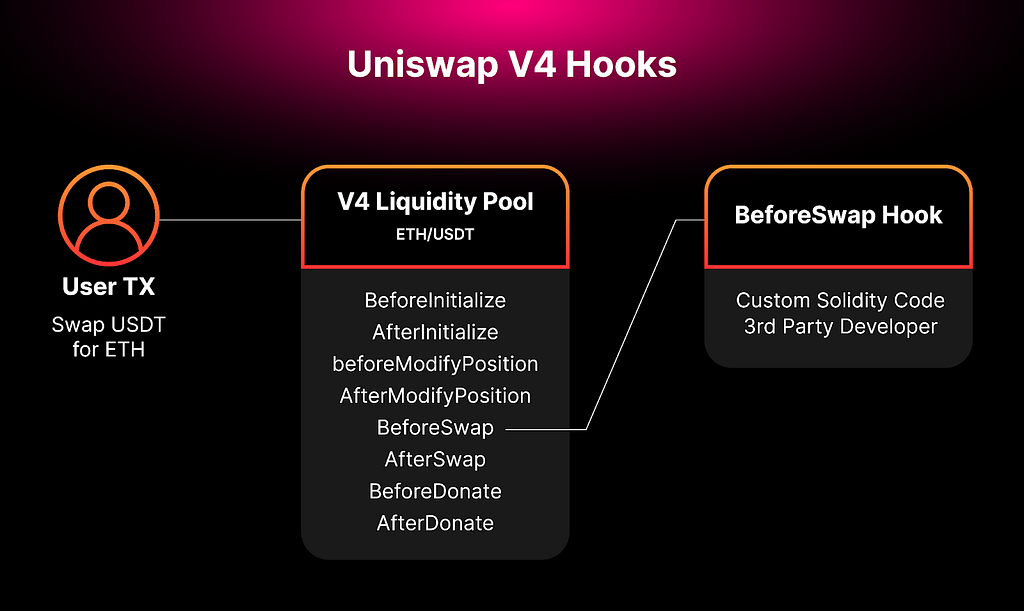
The latest iteration of Uniswap protocol, V4 introduces a brand-new feature called “Hooks” that allows anyone to make these tradeoff decisions by enabling customizable liquidity pools.
What are Hooks?
Hooks are basically code snippets or plugins that enable customization of how pools, swaps, fees, and LP positions interact. They accomplish this by executing specific actions at key stages throughout a pool’s lifecycle. Essentially, by seamlessly integrating with V4’s smart contracts, hooks provide developers with the opportunity to leverage the Uniswap Protocol’s liquidity and security to build personalized AMM pools.
With the implementation of hooks, DeFi users can: –
- Make on-chain limit orders, which are like setting rules for buying and selling assets.
- Automatically put their tokens into lending platforms or reinvest their fees to earn more money.
- Create custom market-making strategies with specific fee structures and pricing rules.
Hooks allow LPs to use their funds more effectively, making Uniswap’s liquidity more versatile. Furthermore, hooks help MEV internalization, which is somewhat similar to a feature called ProtoRev on Osmosis. However, it comes with higher network fees because it involves complex calculations, has slightly weaker guarantees about the order of transactions, and can be more expensive for flash loans.
The Singleton (Consolidation of Pools)
In V3, each market or pool has its own smart contract, making it more expensive to create new markets or even trade across different markets. V4, on the other hand, has a feature called the Singleton that allows any number of markets to live within a single smart contract. This further leads to a reduction in gas fees (by an estimated 99%) as the assets need not be transferred in and out of the markets every time someone swaps. They are moved at the end of the transaction, based on the net balance, making the system more efficient. This system is called “flash accounting”.
These changes and improvements are governed by a new proposal called EIP-1153, which introduces a new way of storing data on Ethereum. This proposal makes utilizing storage — which is only needed for a short time — more straightforward and cost-efficient. This proposal is expected to be part of the next Ethereum upgrade by the end of 2023.
With the efficiency of singleton and flash accounting, fee tiers have become more flexible. Pool creators can choose levels that offer them a competitive edge or even customize them using an effective fee hook. V4 facilitates even more savings on gas fees as it introduces support for native ETH.

Protocol Fee & Governance
Uniswap V4 has made some crucial changes in terms of how fees and governance work. The folks at Uniswap have said:
“As always, we strongly believe that core financial infrastructure should be open and transparent. We also believe that the Uniswap community — the people and teams that support, use, and build on the Protocol — should govern v4 of the Protocol, just as they govern prior versions.”
To put things in perspective, just as in V3, the Uniswap DAO can collect a set percentage of the fee when people swap tokens in a pool. In addition to this, as a new feature in V4, the DAO can also take a set percentage of the fee when people take their money out of a specific pool.
Another big change is that governance no longer has a say on fee levels or how close together the prices can be. This offers more freedom to the pools. Plus, it is now possible to customize withdrawal fees for each pool using hooks, and there’s no standard fee anymore.
Moreover, the Uniswap V4 code will be available with a Business Source Licence 1.1, which limits its commercial for up to four years. After that, it will transit to a GPL license. Moreover, in V4, the governance can vote to decide if they want to add fees to pools, but there.
How Does V4 compare to V3?
Uniswap V4 comes with new features that help traders, market makers, and others in the crypto world. These features make it more flexible, improve how trades are done, and reduce the risk of losing money for liquidity providers.
Some of the key features are summarized below:
- Singleton model: Pools can use their own price data or data from other sources without needing oracles.
- Efficient data storage: It’s better at saving and reading small bits of data, which saves on gas fees.
- Consolidation of Uniswap pools: All Uniswap pools are put together into one place, which makes trading cheaper.
- Flash accounting with EIP-1153: This helps save gas by temporarily changing data during a transaction by avoiding SSTORE operations.
However, some of these features are not entirely new. For instance, the implementation of limit orders is similar to 1inch and Izumi Finance. Furthermore, the Singleton feature that brings together all the pools into a single smart contract, is already present in Balancer V2.
While V4 does make Uniswap more flexible, it doesn’t solve every problem with DEX protocols, like LP impermanent losses and trade quality. In fact, there might be more competition among liquidity providers, which could make transactions more expensive and reduce trade quality, offsetting some of the gas savings.
Overall, owing to features like hooks and the singleton, V4 makes the Uniswap protocol easier to work with and more creative, but it has yet to fix all the issues.
Conclusion
Uniswap V4 marks another milestone in the world of crypto exchange development, offering traders and liquidity providers new tools to enhance their experience. Essentially, Uniswap remains at the forefront of DeFi with its innovative updates.
While Uniswap V4 is still in development, with its draft code available on GitHub, it may be a few months before it’s fully ready to launch. The features we’ve explored in Uniswap V4 are just the beginning of what this new version has to offer. For a more comprehensive understanding of its advancements and possibilities, we encourage you to delve deeper into the whitepaper, where you can grasp the full extent of Uniswap V4’s potential.
To leverage the full potential of DeFi and explore decentralized exchange solutions, consider partnering with our experts in Decentralized Finance Development Services at Codezeros.
Originally published at https://www.codezeros.com.
Uniswap v4: Custom Hooks, Consolidation of Pools, and the Future of DeFi was originally published in Nerd For Tech on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.







