Stock investors have gotten off to a wobbly start to the new year, hobbled by shifting expectations on the timing and extent of Federal Reserve interest-rate cuts in 2024.
All three major U.S. stock indexes snapped a nine-week winning streak on Friday, after unexpectedly strong December job gains prompted traders to briefly pull back on the chances of a March rate cut. The S&P 500
SPX
and Nasdaq Composite
COMP
also failed to stage a Santa Claus Rally from the five final trading days of 2023 through the first two sessions of 2024, as questions grew about the market’s multiple rate-cuts view.
It all adds up to a glimpse of what might be in store for investors in the year ahead. Already, the so-called “January effect,” or theory that stocks tend to rise by more now than any other month, could be put to the test by headwinds that include stalling progress on inflation. Inflation’s downward trend in recent months had given traders and investors hope that as many as six or seven quarter-percentage-point rate cuts from the Federal Reserve could be delivered in 2024, starting in March.
Over the first handful of days in the new year, however, reality has started to sink in. For one thing, multiple rate cuts tend to be more commonly associated with recessions and not soft landings for the economy.
Moreover, the idea that the Fed could follow through with as many rate cuts as envisioned by traders would significantly increase the probability that policymakers lose their battle against inflation, according to Mike Sanders, head of fixed income at Wisconsin-based Madison Investments, which manages $23 billion in assets. That’s because six or more rate cuts would loosen financial conditions by too much, and boost the risk of another bout of inflation that forces officials to hike again, he said.
Minutes of the Fed’s Dec. 12-13 meeting show that policymakers were uncertain about their forecasts for rate cuts this year and failed to rule out the possibility of further rate hikes. Nonetheless, fed funds futures traders continued to cling to expectations for a big decline in borrowing costs, with the greatest likelihood now coalescing around five or six quarter-point rate cuts that total 125 or 150 basis points of easing by year-end. That’s roughly twice as much as what policymakers penciled in last month, when they voted to keep interest rates at a 22-year high of 5.25% to 5.5%.
Source: CME FedWatch Tool, as of Jan. 5.
Uncertainty over the path of U.S. interest rates could leave investors flat-footed once again, and damp the optimism that sent all three major stock indexes in 2023 to their best annual performances of the prior two to three years. In November, analysts at Deutsche Bank AG
DB,
counted seven times since 2021 in which markets expected the Fed to make a dovish pivot, only to be wrong.
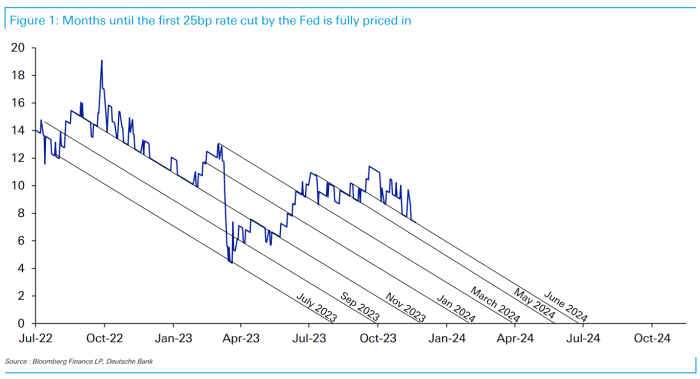
Sources: Bloomberg, Deutsche Bank. Chart is as of Nov. 20, 2023.
Financial markets have been operating with “sky-high expectations” for 2024 rate cuts, but the only way to substantiate six cuts this year is with an “abrupt and sharp downturn in the economy,” said Todd Thompson, managing director and portfolio co-manager at Reams Asset Management in Indianapolis, which oversees $27 billion.
Heading into 2024, euphoria over the prospect of lower borrowing costs produced what Thompson calls “an alarming, everything rally,” which he says leaves equities and high-yield corporate debt vulnerable to pullbacks between now and the next six months. Beyond that period, however, “the trend is likely to be lower rates as the economy finally succumbs to tightening conditions at the same time inflation continues to recede.”
The coming week brings the next major U.S. inflation update, with December’s consumer price index report released on Thursday. The annual headline rate of inflation from CPI has slowed to 3.1% in November from a peak of 9.1% in June 2022. In addition, the core rate from the Fed’s favorite inflation gauge, known as the PCE, has eased to 3.2% year-on-year in November from a 4.2% annual rate in July.
The Fed needs to keep interest rates higher because of all the uncertainty around inflation’s most likely path forward, and the U.S. labor market “won’t degrade fast enough in the first quarter to justify a first rate cut in March,” according to Sanders of Madison Investments.
Rate-cut expectations are “going to be the issue for 2024, and a lot of it is going to be revolving around inflation getting back to that 2% target,” Sanders said via phone. “We think somewhere between 75 and 125 basis points of rate cuts make sense, and that the first move is more of a June-type of event. We don’t think it makes sense to have a March rate cut unless the labor market falls off a cliff.”
History shows that Treasury yields tend to fall in the months leading up to the first rate cut of a Fed easing cycle. However, that isn’t happening right now. Yields on government debt have been on an upward trend since the end of December, with 2-
BX:TMUBMUSD02Y,
10-
BX:TMUBMUSD10Y,
and 30-year yields
BX:TMUBMUSD30Y
ending Friday at their highest levels in more than two to three weeks.
See also: What history says about stocks and the bond market ahead of a first Fed rate cut
While financial markets generally tend to be efficient processors of information, they “haven’t been very accurate in terms of pricing in rate cuts” this time, said Lawrence Gillum, the Charlotte, North Carolina-based chief fixed-income strategist for broker-dealer for LPL Financial. He said the big risk for 2024 is if financial conditions ease too much and the Fed declares victory on inflation too soon, which could reignite price pressures in a manner reminiscent of the 1970s period under former Fed Chairman Arthur Burns.
“We think rate-cut expectations have gone too far too fast, and that the backup in yields we are seeing right now is the market acknowledging that maybe rate cuts are not going to be as aggressive as what was priced in,” Gillum said via phone.
December’s CPI report on Thursday is the data highlight of the week ahead.
On Monday, consumer-credit data for November is set to be released, followed the next day by trade-deficit figures for the same month.
Wednesday brings the wholesale-inventories report for November and remarks by New York Fed President John Williams.
Initial weekly jobless claims are released on Thursday. On Friday, the producer price index for December comes out.